Pembrolizumab therapy in a patient with NSCLC and bullous pemphigoid: A case report
- PMID: 39139747
- PMCID: PMC11319822
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2024.14603
Pembrolizumab therapy in a patient with NSCLC and bullous pemphigoid: A case report
Abstract
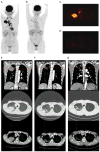
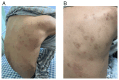
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, which targets programmed cell death protein 1, has demonstrated enhanced survival outcomes in numerous patients with cancer. Historically, individuals with autoimmune diseases have been excluded from clinical trials involving cancer immunotherapies due to concerns about the potential worsening of their underlying autoimmune conditions. In the present case report, a patient with non-small cell lung cancer and bullous pemphigoid (BP) who underwent treatment with the ICI pembrolizumab is described. In this specific clinical case, no severe exacerbation of the underlying autoimmune disease was observed. Contrarily, the patient not only tolerated pembrolizumab well but also experienced amelioration of the BP lesions after the treatment. This case challenges the conventional exclusion criteria for ICI therapy in patients with autoimmune diseases, suggesting the potential safety and efficacy of such treatments in this specific population. However, further investigations and larger-scale studies are warranted to validate these findings and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the implications of ICI therapy in patients with autoimmune comorbidities.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; bullous pemphigoid; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer; pembrolizumab.
Copyright: © 2024 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Reckamp KL, Redman MW, Dragnev KH, Minichiello K, Villaruz LC, Faller B, Al Baghdadi T, Hines S, Everhart L, Highleyman L, et al. Phase II randomized study of ramucirumab and pembrolizumab versus standard of care in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with immunotherapy-lung-MAP S1800A. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:2295–2306. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.9004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xing P, Wang M, Zhao J, Zhong W, Chi Y, Xu Z, Li J. Study protocol: A single-arm, multicenter, phase II trial of camrelizumab plus apatinib for advanced nonsquamous NSCLC previously treated with first-line immunotherapy. Thorac Cancer. 2021;12:2825–2828. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
