Adolescent pilonidal disease laser treatment (a-PiLaT): a pilot study
- PMID: 39141158
- PMCID: PMC11324676
- DOI: 10.1007/s10151-024-02972-w
Adolescent pilonidal disease laser treatment (a-PiLaT): a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Pilonidal disease (PD) is an acquired condition related to hair-induced mechanical forces on the skin surface of the intergluteal cleft, with subsequent abscess formation with or without a concomitant draining sinus (pit). While surgical management currently is the mainstay of treatment, pilonidal disease laser treatment (PiLaT) has recently been recognized as a promising treatment option for non-inflammatory diseases. Nonetheless, there is a paucity of available data on adolescent pilonidal disease laser treatment (a-PiLaT).
Methods: We describe our preliminary experience with PiLaT performed in adolescents aged 10-17 years at our tertiary paediatric surgical hospital from 2019 to 2023. Data on perioperative characteristics and clinical outcomes at follow-up were retrospectively analysed.
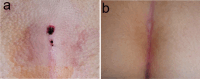
Results: A total of 17 consecutive patients (n = 12 female, 71%) underwent a-PiLaT. At the time of treatment, the patients' mean age and body mass index were 13.6 ± 1.6 years and 25.3 ± 5.6 kg m-2, respectively. The mean operative time was 21.5 ± 10.4 min, whereas the mean follow-up period was 24.5 ± 16.8 months, with a complication rate of 24% (n = 4) and recurrence rate of 18% (n = 3). With respect to postsurgical scar assessment, the mean Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale scores (score range 6-60, with higher scores indicating worse outcome) were 14.2 ± 6.5 (patients' evaluation) and 11.4 ± 4.7 (observers' evaluation).
Conclusion: The a-PiLaT represents a novel approach for managing PD in adolescents. Our preliminary data on the outcomes of a small series of patients with pilonidal sinuses after a-PiLaT indicated complication and recurrence rates comparable to those reported in the literature for adults. This new minimally invasive technique has great potential and is therefore worthy of further research on a larger population.
Keywords: Adolescent surgery; Laser; Pilonidal cyst; Pilonidal disease.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Karydakis GE (1992) Easy and successful treatment of pilonidal sinus after explanation of its causative process. Aust N Z J Surg 62:385–389 - PubMed
-
- Bascom J (1983) Pilonidal disease: long-term results of follicle removal. Dis Colon Rectum 26:800–807 - PubMed
-
- Bascom J (1994) Pilonidal sinus. Curr Pract Surg 6:175–180
-
- Özkan Z, Aksoy N, Emir S (2014) Investigation of the relationship between serum hormones and pilonidal sinus disease: a cross-sectional study. Colorectal Dis 16(4):311–314 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources