How to distinguish promotion, prevention and treatment trials in public mental health? Study protocol for the development of the VErona-LUgano Tool (VELUT)
- PMID: 39142679
- PMCID: PMC11332010
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-082652
How to distinguish promotion, prevention and treatment trials in public mental health? Study protocol for the development of the VErona-LUgano Tool (VELUT)
Abstract
Introduction: Promoting mental health, preventing and treating mental disorders are critically important in public health, and many randomised controlled trials (RCTs) evaluate intervention strategies for these objectives. However, distinguishing promotion from prevention and from treatment RCTs is challenging. A tool to place studies along the promotion-to-treatment continuum in mental health research does not exist, leaving it to researchers and policymakers to decide on how to classify individual RCTs, which hinders evidence synthesis.
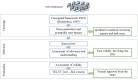
Methods and analysis: We present a protocol for the development of a new tool to assist researchers in distinguishing RCTs along the promotion-to-treatment continuum. We will establish a Tool Development Group, and use the Population, Intervention, Comparison and Outcome framework to define constructs. We will generate, define, categorise and reduce the items in the tool using qualitative methods, including cognitive interviews and a Delphi exercise. Psychometric evaluation-including unidimensionality, local independence, monotonicity and item homogeneity-will include data collection, scoring, internal consistency checks and factor analysis of the tool's indicators for available RCTs. We will use standard Cohen's kappa statistics to assess the reliability of the tool.
Ethics and dissemination: This study involves data collection from the already published literature. However, this protocol has been approved by the ethics committee of the Università della Svizzera Italiana (CE 2024 04). The results of the present project will be disseminated in peer-reviewed journals and at international and national scientific meetings. Training materials for the application of the tool will also be developed and disseminated to the scientific community. The tool and all related implementation materials will be published on a website and will be freely accessible to the public.
Keywords: MENTAL HEALTH; PUBLIC HEALTH; Psychometrics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Prevention of Mental Disorders . In: Reducing risks for mental disorders: frontiers for preventive intervention research. Mrazek PJ, Haggerty RJ, editors. National Academies Press (US); 1994. - PubMed
-
- National Research Council (US), Institute of Medicine Committee (US) on the Prevention of Mental Disorders and Substance Abuse Among Children, Youth, and Young Adults: Research Advances and Promising Interventions; The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health . In: Preventing mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders among young people: progress and possibilities. O’Connell ME, Boat T, Warner KE, editors. Washington(DC): National Academies Press (US) Copyright © 2009, National Academy of Sciences; 2009.
-
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education; Board on Children, Youth and Families et al . Fostering healthy mental, emotional, and behavioral development in children and youth: a national agenda. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US) Copyright © 2019, National Academy of Sciences; 2019. - PubMed
-
- Eaton WW. Public mental health. Oxford University Press; 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical