A spatiotemporally resolved atlas of mRNA decay in the C. elegans embryo reveals differential regulation of mRNA stability across stages and cell types
- PMID: 39142810
- PMCID: PMC11444186
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.278980.124
A spatiotemporally resolved atlas of mRNA decay in the C. elegans embryo reveals differential regulation of mRNA stability across stages and cell types
Abstract
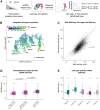
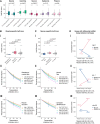
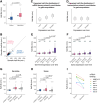
During embryonic development, cells undergo dynamic changes in gene expression that are required for appropriate cell fate specification. Although both transcription and mRNA degradation contribute to gene expression dynamics, patterns of mRNA decay are less well understood. Here, we directly measure spatiotemporally resolved mRNA decay rates transcriptome-wide throughout C. elegans embryogenesis by transcription inhibition followed by bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing. This allows us to calculate mRNA half-lives within specific cell types and developmental stages, and identify differentially regulated mRNA decay throughout embryonic development. We identify transcript features that are correlated with mRNA stability and find that mRNA decay rates are associated with distinct peaks in gene expression over time. Moreover, we provide evidence that, on average, mRNA is more stable in the germline than in the soma and in later embryonic stages than in earlier stages. This work suggests that differential mRNA decay across cell states and time helps to shape developmental gene expression, and it provides a valuable resource for studies of mRNA turnover regulatory mechanisms.
© 2024 Peng et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures





Update of
-
A spatiotemporally resolved atlas of mRNA decay in the C. elegans embryo reveals differential regulation of mRNA stability across stages and cell types.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 16:2024.01.15.575757. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.15.575757. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Genome Res. 2024 Sep 20;34(8):1235-1252. doi: 10.1101/gr.278980.124. PMID: 38293118 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
A spatiotemporally resolved atlas of mRNA decay in the C. elegans embryo reveals differential regulation of mRNA stability across stages and cell types.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 16:2024.01.15.575757. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.15.575757. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Genome Res. 2024 Sep 20;34(8):1235-1252. doi: 10.1101/gr.278980.124. PMID: 38293118 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
EDC-3 and EDC-4 regulate embryonic mRNA clearance and biomolecular condensate specialization.Cell Rep. 2024 Oct 22;43(10):114781. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114781. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39331503
-
Gene regulatory patterning codes in early cell fate specification of the C. elegans embryo.Elife. 2024 Jan 29;12:RP87099. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87099. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38284404 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology of embryonic development: Prospects for a complete understanding of the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2018 May;7(3):e314. doi: 10.1002/wdev.314. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29369536 Review.
-
Germ versus soma decisions: lessons from flies and worms.Science. 2007 Apr 20;316(5823):392-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1140846. Science. 2007. PMID: 17446385 Review.
Cited by
-
Landscape and regulation of mRNA translation in the early C. elegans embryo.Cell Rep. 2025 Jun 24;44(6):115778. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115778. Epub 2025 May 30. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40450690 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape and regulation of mRNA translation in the early C. elegans embryo.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 1:2024.12.13.628416. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.13.628416. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cell Rep. 2025 Jun 24;44(6):115778. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115778. PMID: 39829802 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
