Abstract representations emerge in human hippocampal neurons during inference
- PMID: 39143207
- PMCID: PMC11338822
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07799-x
Abstract representations emerge in human hippocampal neurons during inference
Abstract
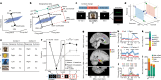
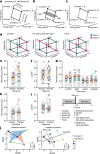
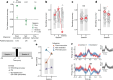
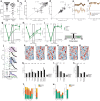
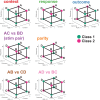
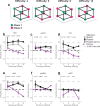
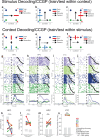
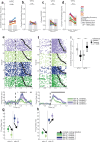
Humans have the remarkable cognitive capacity to rapidly adapt to changing environments. Central to this capacity is the ability to form high-level, abstract representations that take advantage of regularities in the world to support generalization1. However, little is known about how these representations are encoded in populations of neurons, how they emerge through learning and how they relate to behaviour2,3. Here we characterized the representational geometry of populations of neurons (single units) recorded in the hippocampus, amygdala, medial frontal cortex and ventral temporal cortex of neurosurgical patients performing an inferential reasoning task. We found that only the neural representations formed in the hippocampus simultaneously encode several task variables in an abstract, or disentangled, format. This representational geometry is uniquely observed after patients learn to perform inference, and consists of disentangled directly observable and discovered latent task variables. Learning to perform inference by trial and error or through verbal instructions led to the formation of hippocampal representations with similar geometric properties. The observed relation between representational format and inference behaviour suggests that abstract and disentangled representational geometries are important for complex cognition.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Update of
-
Abstract representations emerge in human hippocampal neurons during inference behavior.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 30:2023.11.10.566490. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.10.566490. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8026):841-849. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07799-x. PMID: 37986878 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

