Moderate hypofractionated radiotherapy to the prostate bed with or without pelvic lymph nodes: a prospective trial
- PMID: 39143977
- PMCID: PMC11321776
- DOI: 10.5603/rpor.99677
Moderate hypofractionated radiotherapy to the prostate bed with or without pelvic lymph nodes: a prospective trial
Abstract
Background: Hypofractionated radiotherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer has been widely studied. However, in the postoperative setting it has been less explored. The objective of this prospective study is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of hypofractionated radiotherapy in postoperative prostate cancer.
Materials and methods: A prospective study was designed to include patients with prostate cancer with an indication of postoperative radiotherapy as adjuvant or salvage. A hypofractionated radiotherapy scheme of 51 Gy in 17 fractions was performed with the possibility of treating the pelvis at a dose of 36 Gy in 12 fractions sequentially. Safety was evaluated based on acute and late toxicity [according to the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) scale and Common Terminology Criteria Adverse Events (CTCAE) v4.03], International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) over time, and quality of life.
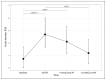
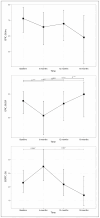
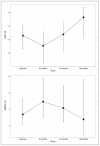
Results: From August 2020 to June 2022, 31 patients completed treatment and were included in this report. 35.5% of patients received elective treatment of the pelvic nodal areas. Most patients reported minimal or low acute toxicity, with an acute gastrointestinal (GI) and genitourinary (GU) grade 3 or greater toxicity of 3.2% and 0%, respectively. The evolution in time of the IPSS remained without significant differences (p = 0.42). With the exception of a significant improvement in the domains of hormonal and sexual symptoms of the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC) questionnaire, the rest of the domains [EPIC, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Core quality of life questionnaire (C-30) and Prostate Cancer module (PR-25)] were maintained without significant differences over time. With a follow-up of 15.4 months, late GI and GU grade 2 toxicity was reported greater than 0% and 9.6%, respectively.
Conclusions: Hypofractionated radiotherapy in postoperative prostate cancer appears to be safe with low reports of relevant acute or late toxicity. Further follow-up is required to confirm these results.
Trial registration: The protocol was approved by the accredited Medical Ethical Committee of Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile. All participants accepted and wrote informed consent.
Keywords: hypofractionated radiotherapy; postoperative radiotherapy; prostate cancer.
© 2024 Greater Poland Cancer Centre.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Globocan. International Agency for Research on Cancer World Health Organization; 2018.
-
- Bolla M, van Poppel H, Tombal B, et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer, Radiation Oncology and Genito-Urinary Groups. Postoperative radiotherapy after radical prostatectomy for high-risk prostate cancer: long-term results of a randomised controlled trial (EORTC trial 22911) Lancet. 2012;380(9858):2018–2027. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61253-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thompson IM, Tangen CM, Paradelo J, et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy for pathological T3N0M0 prostate cancer significantly reduces risk of metastases and improves survival: long-term followup of a randomized clinical trial. J Urol. 2009;181(3):956–962. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.11.032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
