The monkeypox virus-host interplays
- PMID: 39144256
- PMCID: PMC11321328
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellin.2024.100185
The monkeypox virus-host interplays
Abstract
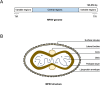
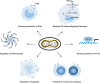
Monkeypox virus (MPXV) is a DNA virus belonging to the Orthopoxvirus genus within the Poxviridae family which can cause a zoonotic infection. The unexpected non-endemic outbreak of mpox in 2022 is considered as a new global threat. It is imperative to take proactive measures, including enhancing our understanding of MPXV's biology and pathogenesis, and developing novel antiviral strategies. The host immune responses play critical roles in defensing against MPXV infection while the virus has also evolved multiple strategies for immune escape. This review summarizes the biological features, antiviral immunity, immune evasion mechanisms, pathogenicity, and prevention strategies for MPXV.
Keywords: Antiviral immunity; Immune evasion; Monkeypox virus; Pathogenicity.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Wuhan University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Adamo S., Gao Y., Sekine T., Mily A., Wu J., Storgard E., Westergren V., Filen F., Treutiger C.J., Sandberg J.K., Sallberg M., Bergman P., Llewellyn-Lacey S., Ljunggren H.G., Price D.A., Ekstrom A.M., Sette A., Grifoni A., Buggert M. Memory profiles distinguish cross-reactive and virus-specific T cell immunity to mpox. Cell Host Microbe. 2023;31(6):928–936 e4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adler H., Gould S., Hine P., Snell L.B., Wong W., Houlihan C.F., Osborne J.C., Rampling T., Beadsworth M.B., Duncan C.J., Dunning J., Fletcher T.E., Hunter E.R., Jacobs M., Khoo S.H., Newsholme W., Porter D., Porter R.J., Ratcliffe L., Network, N.H.S.E.H.C.I.D. Clinical features and management of human monkeypox: A retrospective observational study in the UK. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2022;22(8):1153–1162. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

