Detecting image manipulation with ELA-CNN integration: a powerful framework for authenticity verification
- PMID: 39145198
- PMCID: PMC11323046
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2205
Detecting image manipulation with ELA-CNN integration: a powerful framework for authenticity verification
Abstract
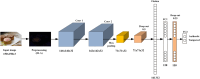
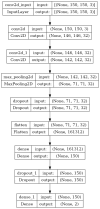
The exponential progress of image editing software has contributed to a rapid rise in the production of fake images. Consequently, various techniques and approaches have been developed to detect manipulated images. These methods aim to discern between genuine and altered images, effectively combating the proliferation of deceptive visual content. However, additional advancements are necessary to enhance their accuracy and precision. Therefore, this research proposes an image forgery algorithm that integrates error level analysis (ELA) and a convolutional neural network (CNN) to detect the manipulation. The system primarily focuses on detecting copy-move and splicing forgeries in images. The input image is fed to the ELA algorithm to identify regions within the image that have different compression levels. Afterward, the created ELA images are used as input to train the proposed CNN model. The CNN model is constructed from two consecutive convolution layers, followed by one max pooling layer and two dense layers. Two dropout layers are inserted between the layers to improve model generalization. The experiments are applied to the CASIA 2 dataset, and the simulation results show that the proposed algorithm demonstrates remarkable performance metrics, including a training accuracy of 99.05%, testing accuracy of 94.14%, precision of 94.1%, and recall of 94.07%. Notably, it outperforms state-of-the-art techniques in both accuracy and precision.
Keywords: CNN; Copy-move; ELA; Forgery; Image splicing; Tampering.
© 2024 Nagm et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abd Warif NB, Idris MYI, Wahab AWA, Salleh R. An evaluation of error level analysis in image forensics. 2015 5th IEEE International Conference on System Engineering and Technology (ICSET); Piscataway: IEEE; 2015. pp. 23–28.
-
- Alahmadi AA, Hussain M, Aboalsamh H, Muhammad G, Bebis G. Splicing image forgery detection based on dct and local binary pattern. 2013 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing; Piscataway: IEEE; 2013. pp. 253–256.
-
- Alahmadi A, Hussain M, Aboalsamh H, Muhammad G, Bebis G, Mathkour H. Passive detection of image forgery using DCT and local binary pattern. Signal, Image and Video Processing. 2017;11(1):81–88. doi: 10.1007/s11760-016-0899-0. - DOI
-
- Alberry HA, Hegazy AA, Salama GI. A fast SIFT based method for copy move forgery detection. Future Computing and Informatics Journal. 2018;3(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/j.fcij.2018.03.001. - DOI
-
- Ali SS, Ganapathi II, Vu N-S, Ali SD, Saxena N, Werghi N. Image forgery detection using deep learning by recompressing images. Electronics. 2022;11(3):403. doi: 10.3390/electronics11030403. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
