CD8 + T-cell deficiency protects mice from abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in response to calcium chloride 2
- PMID: 39146540
- PMCID: PMC11451972
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003823
CD8 + T-cell deficiency protects mice from abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in response to calcium chloride 2
Abstract
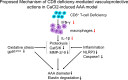
Objective: Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is an aneurysm-like dilated and highly fatal cardiovascular disease. CD8 + T cells have been shown to be critical for vascular pathological processes, but the contribution of these lymphocytes to vascular diseases remains elusive.
Methods and results: Eight-week-old male wildtype (CD8 +/+ ) and Cd8a knockout (CD8 -/- ) mice were used in a calcium chloride 2 (CaCl 2 )-induced experimental AAA model. At 6 weeks after surgery, CD8 + T-cell deletion prevented the formation of AAA, accompanied by reductions of the levels of inflammatory (interferon-γ [IFN-γ], interleukin-1β, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, intracellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, NOD-like receptor protein 3, caspase-1), oxidative stress [NADPH oxidase and gp91 phox ], and proteolysis (cathepsin S, cathepsin K, matrix metalloproteinase-2 [MMP-2] and MMP-9) proteins and/or genes in plasma and/or AAA tissues. Immunoreactivities of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were observed in macrophages. An injection of IFN-γ and adoptive transfer of CD8 + T cells of IFN-γ +/+ mice diminished CD8 -/- -mediated vasculoprotective actions in the AAA mice. In vitro, IFN-γ enhanced MMP-2 and MMP-9 gelatinolytic activities in macrophage and/or vascular smooth muscle cells.
Conclusion: The vasculoprotective effects of CD8 + T-cell deletion in a mouse CaCl 2 -induced AAA model were likely attributable to, at least in part, the attenuation of IFN-γ-dependent inflammation action, oxidative stress production, and proteolysis, suggesting a novel therapeutic target for AAA formation by regulating CD8 + T-cell-derived IFN-γ secretion.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships or conflicts of interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures





References
-
- Lu Y, Ma Q, Tan H, Li X, Zhang X, Tie Y. Specific inhibition of SHP2 suppressed abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in mice by augmenting the immunosuppressive function of MDSCs. Life Sci 2021; 265:118751. - PubMed
-
- Sakalihasan N, Michel JB, Katsargyris A, Kuivaniemi H, Defraigne JO, Nchimi A, et al. . Abdominal aortic aneurysms. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018; 4:34. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H, Sasaki T, Jin E, Kuzuya M, Cheng XW. Inflammatory cells and proteases in abdominal aortic aneurysm and its complications. Curr Drug Targets 2018; 19:1289–1296. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

