SARS-CoV2 infection in whole lung primarily targets macrophages that display subset-specific responses
- PMID: 39147987
- PMCID: PMC11335275
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05322-z
SARS-CoV2 infection in whole lung primarily targets macrophages that display subset-specific responses
Abstract
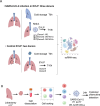
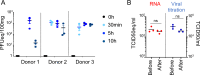
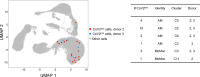
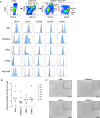
Deciphering the initial steps of SARS-CoV-2 infection, that influence COVID-19 outcomes, is challenging because animal models do not always reproduce human biological processes and in vitro systems do not recapitulate the histoarchitecture and cellular composition of respiratory tissues. To address this, we developed an innovative ex vivo model of whole human lung infection with SARS-CoV-2, leveraging a lung transplantation technique. Through single-cell RNA-seq, we identified that alveolar and monocyte-derived macrophages (AMs and MoMacs) were initial targets of the virus. Exposure of isolated lung AMs, MoMacs, classical monocytes and non-classical monocytes (ncMos) to SARS-CoV-2 variants revealed that while all subsets responded, MoMacs produced higher levels of inflammatory cytokines than AMs, and ncMos contributed the least. A Wuhan lineage appeared to be more potent than a D614G virus, in a dose-dependent manner. Amidst the ambiguity in the literature regarding the initial SARS-CoV-2 cell target, our study reveals that AMs and MoMacs are dominant primary entry points for the virus, and suggests that their responses may conduct subsequent injury, depending on their abundance, the viral strain and dose. Interfering on virus interaction with lung macrophages should be considered in prophylactic strategies.
Keywords: 10X genomics; Azimuth software; Ex vivo lung perfusion; Viral nebulization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

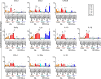
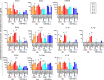
References
-
- Delorey TM, Ziegler CGK, Heimberg G, Normand R, Yang Y, Segerstolpe A, Abbondanza D, Fleming SJ, Subramanian A, Montoro DT et al (2021) COVID-19 tissue atlases reveal SARS-CoV-2 pathology and cellular targets. Nature 595:107–113. 10.1038/s41586-021-03570-8 10.1038/s41586-021-03570-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar J, Gary J, Reagan-Steiner S, Estetter LB, Tong S, Tao Y, Denison AM, Lee E, DeLeon-Carnes M, Li Y et al (2021) Evidence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 replication and tropism in the lungs, airways, and vascular endothelium of patients with fatal coronavirus disease 2019: an autopsy case series. J Infect Dis 223:752–764. 10.1093/infdis/jiab039 10.1093/infdis/jiab039 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

