Exosomal lncRNAs as regulators of breast cancer chemoresistance and metastasis and their potential use as biomarkers
- PMID: 39148900
- PMCID: PMC11324554
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1419808
Exosomal lncRNAs as regulators of breast cancer chemoresistance and metastasis and their potential use as biomarkers
Abstract
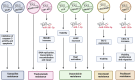
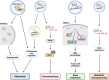
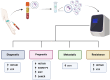
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women and the leading cause of female deaths by cancer in the world worldwide. Hence, understanding the molecular mechanisms associated with breast cancer development and progression, including drug resistance and breast cancer metastasis, is essential for achieving the best management of breast cancer patients. Cancer-related long noncoding RNAs have been shown to be involved in the regulation of each stage of breast cancer progression. Additionally, exosomes are extracellular microvesicles that are central to intercellular communication and play an important role in tumorigenesis. Exosomes can be released from primary tumor cells into the bloodstream and transmit cellular signals to distant body sites. In this work, we review the findings regarding the cellular mechanisms regulated by exosomal lncRNAs that are essentials to chemoresistance development and metastasis of breast cancer. Likewise, we evaluate the outcomes of the potential clinical use of exosomal lncRNAs as breast cancer biomarkers to achieve personalized management of the patients. This finding highlights the importance of transcriptomic analysis of exosomal lncRNAs to understand the breast cancer tumorigenesis as well as to improve the clinical tests available for this disease.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer biomarkers; chemoresistance; exosomes; lncRNA; metastasis.
Copyright © 2024 Blancas-Zugarazo, Langley and Hidalgo-Miranda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNAs and exosomal lncRNAs: classification, and mechanisms in breast cancer metastasis and drug resistance.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(5):953-974. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1040-y. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31601996 Review.
-
Biological functions and clinical applications of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(20):11656-11666. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15873. Epub 2020 Sep 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32924276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of exosomal lncRNAs in cancer biology and clinical management.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Nov;53(11):1669-1673. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00699-4. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34819615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes and exosomal RNAs in breast cancer: A status update.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Feb;144:252-268. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.11.033. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33373870 Review.
-
Exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer: Interplay, modulation, and therapeutic avenues.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Apr 4;9(3):887-900. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.03.014. eCollection 2024 Sep. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 38616862 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes and breast cancer angiogenesis; Highlights in intercellular communication.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03606-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39696346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Exosome in Solid Cancer Progression and Its Potential Therapeutics in Cancer Treatment.Cancer Med. 2025 May;14(9):e70941. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70941. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40344389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNAs in familial hypercholesterolemia: biomarkers, therapeutics, and AI in precision medicine.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 May 21;24(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02605-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40399983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC01559: roles, mechanisms, and clinical implications in human cancers.Hum Cell. 2025 Apr 9;38(3):83. doi: 10.1007/s13577-025-01218-7. Hum Cell. 2025. PMID: 40205068 Review.
References
-
- Global cancer observatory. GLOBOCAN; (2022). Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

