Eosinophil extracellular vesicles and DNA traps in allergic inflammation
- PMID: 39148911
- PMCID: PMC11324581
- DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2024.1448007
Eosinophil extracellular vesicles and DNA traps in allergic inflammation
Abstract
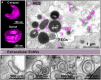
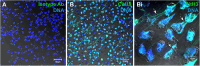
Eosinophil granulocytes, a specialized subset of white blood cells, have traditionally been associated with allergic responses and parasitic infections. However, recent research has unveiled their versatile roles in immune regulation beyond these classical functions. This review highlights the emerging field of eosinophil biology, with a particular focus on their release of extracellular vesicles (EVs) and extracellular DNA traps (EETs). It further explores potential implications of eosinophil-derived EVs and EETs for immune responses during inflammatory diseases. The release of EVs/EETs from eosinophils, which also affects the eosinophils themselves, may influence both local and systemic immune reactions, affecting the pathophysiology of conditions such as airway inflammation, chronic rhinosinusitis and atopic dermatitis.
Keywords: EETosis; eosinophil activation; eosinophilic diseases; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; sombrero vesicles.
© 2024 Weihrauch, Melo, Gray, Voehringer, Weller and Raap.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Ehrlich P. Ueber die spezifischen granulationen des blutes. Arch Anat Physiol Physiol Abt. (1879):571–9.
-
- Melo RCN. Eosinophil Ultrastructure: Atlas of Eosinophil Cell Biology and Pathology. San Diego: Elsevier Science & Technology; (2022).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

