Separation and purification of nylon 54 salts from fermentation broth by an integrated process involving microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and ion exchange
- PMID: 39148940
- PMCID: PMC11324497
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1448927
Separation and purification of nylon 54 salts from fermentation broth by an integrated process involving microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and ion exchange
Abstract
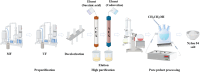
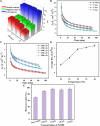
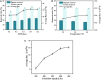
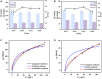
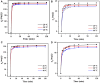
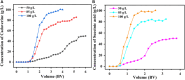
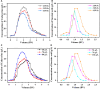
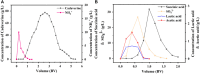
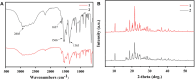
Nylon 54 is a novel, biodegradable polyamide with excellent thermal resistance and water absorption properties. It can be polymerized using bio-based cadaverine and succinic acid as monomers. Traditional separation methods isolate individual monomers from the fermentation broth through acidification or alkalization, resulting in significant amounts of waste salts; however, synchronous separation of dibasic acids and diamines has not been reported. This study investigated an integrated process for the separation and extraction of nylon 54 salts from a co-fermentation broth without acidification or alkalization. We meticulously optimized the operational parameters of the integrated process to achieve maximum separation efficiency. Following microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and decolorization, the bacterial eliminating rate was ≥99.83%, and the protein concentration was ≤40 mg/L. The absorbance of the decolorized solution was ≤0.021 at 430 nm, and the recovery rate of nylon 54 salt reached 97%. Then, the pretreated solution was passed through sequential chromatographic columns, which effectively removed organic acid by-products (such as acetic acid and lactic acid), SO4 2-, and NH4 + from the fermentation broth, resulting in a cadaverine yield of 98.01% and a succinic acid yield of 89.35%. Finally, by concentrating and crystallizing the eluent, the simulated fermentation broth yielded nylon 54 salt with a purity of 99.16% and a recovery rate of 58%, and the real fermentation broth yielded nylon 54 salt with a purity of 98.10% and a recovery rate of 56.21%. This integrated process offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly pathway for the complete biosynthesis of nylon 54 salt and has the potential to be extended to the preparation of other nylon salts.
Keywords: crystallization; fermentation broth separation; ion exchange resin; membrane separation; nylon 54 salt.
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Hu, Yang, Feng, Wang, Li, Li and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coupling the fermentation and membrane separation process for polyamides monomer cadaverine production from feedstock lysine.Eng Life Sci. 2021 Jun 10;21(10):623-629. doi: 10.1002/elsc.202000099. eCollection 2021 Oct. Eng Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34690633 Free PMC article.
-
Separation and purification of γ-aminobutyric acid from fermentation broth by flocculation and chromatographic methodologies.J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Feb 27;61(8):1914-9. doi: 10.1021/jf304749v. Epub 2013 Feb 12. J Agric Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 23402360
-
Novel chromatographic purification of succinic acid from whey fermentation broth by anionic exchange resins.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2022 Dec;45(12):2007-2017. doi: 10.1007/s00449-022-02805-w. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2022. PMID: 36352044
-
Lactic acid separation and recovery from fermentation broth by ion-exchange resin: A review.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021 Apr 20;8(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40643-021-00384-4. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2021. PMID: 38650212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recovery of carboxylic acids produced by fermentation.Biotechnol Adv. 2014 Sep-Oct;32(5):873-904. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Biotechnol Adv. 2014. PMID: 24751382 Review.
References
-
- Ahmad A., Othman I., Taher H., Banat F. (2021). Lactic acid recovery from date pulp waste fermentation broth by ions exchange resins. Environ. Technol. Innov. 22, 101438. 10.1016/j.eti.2021.101438 - DOI
-
- Anwar S., Hassanpour Amiri M., Jiang S., Abolhasani M. M., Rocha P. R. F., Asadi K. (2020). Piezoelectric nylon‐11 fibers for electronic textiles, energy harvesting and sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater 31, 2004326. 10.1002/adfm.202004326 - DOI
-
- Can C. E., Zeidan H., Marti M. E. (2024). Efficient recovery of itaconic acid using weak and strong anion exchange resins from aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 63, 5833–5844. 10.1021/acs.iecr.3c04158 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

