This is a preprint.
Centrocortin potentiates co-translational localization of its mRNA to the centrosome via dynein
- PMID: 39149256
- PMCID: PMC11326273
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.08.09.607365
Centrocortin potentiates co-translational localization of its mRNA to the centrosome via dynein
Abstract
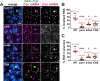
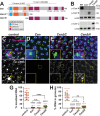
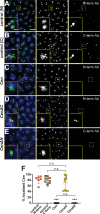
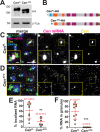
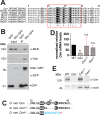
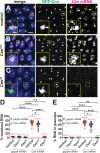
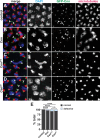
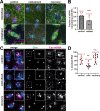
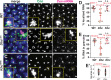
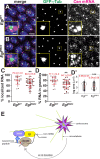
Centrosomes rely upon proteins within the pericentriolar material to nucleate and organize microtubules. Several mRNAs also reside at centrosomes, although less is known about how and why they accumulate there. We previously showed that local Centrocortin (Cen) mRNA supports centrosome separation, microtubule organization, and viability in Drosophila embryos. Here, using Cen mRNA as a model, we examine mechanisms of centrosomal mRNA localization. We find that while the Cen N'-terminus is sufficient for protein enrichment at centrosomes, multiple domains cooperate to concentrate Cen mRNA at this location. We further identify an N'-terminal motif within Cen that is conserved among dynein cargo adaptor proteins and test its contribution to RNA localization. Our results support a model whereby Cen protein enables the accumulation of its own mRNA to centrosomes through a mechanism requiring active translation, microtubules, and the dynein motor complex. Taken together, our data uncover the basis of translation-dependent localization of a centrosomal RNA required for mitotic integrity.
Keywords: RNA localization; cargo adaptor; centrosome; dynein; transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Apweiler R., Attwood T.K., Bairoch A., Bateman A., Birney E., Biswas M., Bucher P., Cerutti L., Corpet F., Croning M.D., Durbin R., Falquet L., Fleischmann W., Gouzy J., Hermjakob H., Hulo N., Jonassen I., Kahn D., Kanapin A., Karavidopoulou Y., Lopez R., Marx B., Mulder N.J., Oinn T.M., Pagni M., Servant F., Sigrist C.J., Zdobnov E.M., and InterPro C.. 2000. InterPro--an integrated documentation resource for protein families, domains and functional sites. Bioinformatics. 16:1145–1150. - PubMed
-
- Bellen H.J., Levis R.W., Liao G., He Y., Carlson J.W., Tsang G., Evans-Holm M., Hiesinger P.R., Schulze K.L., Rubin G.M., Hoskins R.A., and Spradling A.C.. 2004. The BDGP gene disruption project: single transposon insertions associated with 40% of Drosophila genes. Genetics. 167:761–781. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergalet J., Patel D., Legendre F., Lapointe C., Benoit Bouvrette L.P., Chin A., Blanchette M., Kwon E., and Lecuyer E.. 2020. Inter-dependent Centrosomal Co-localization of the cen and ik2 cis-Natural Antisense mRNAs in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 30:3339–3352 e3336. - PubMed
-
- Besse F., and Ephrussi A.. 2008. Translational control of localized mRNAs: restricting protein synthesis in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:971–980. - PubMed
-
- Bolte S., and Cordelieres F.P.. 2006. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J Microsc. 224:213–232. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
