This is a preprint.
Inhibitory basal ganglia nuclei differentially innervate pedunculopontine nucleus subpopulations and evoke differential motor and valence behaviors
- PMID: 39149277
- PMCID: PMC11326182
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.08.05.606694
Inhibitory basal ganglia nuclei differentially innervate pedunculopontine nucleus subpopulations and evoke differential motor and valence behaviors
Update in
-
Inhibitory basal ganglia nuclei differentially innervate pedunculopontine nucleus subpopulations and evoke differential motor and valence behaviors.Elife. 2025 Aug 20;13:RP102308. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102308. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40833252 Free PMC article.
Abstract
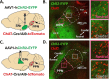
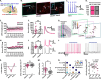
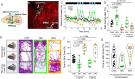
The canonical basal ganglia model predicts that the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) and the globus pallidus externa (GPe) will have specific effects on locomotion: the SNr inhibiting locomotion and the GPe enhancing it. In this study, we use in vivo optogenetics to show that the GPe exerts non-canonical effects on locomotion while the SNr has no gross motor impact through inhibition of the PPN. We also show that these structures mediate opposing effects on reward. To understand how these structures differentially modulate the PPN, we use ex vivo whole-cell recording with optogenetics to comprehensively dissect the SNr and GPe synaptic connections to regionally- and molecularly-defined populations of PPN neurons. The SNr inhibits all PPN subtypes, but most strongly inhibits caudal glutamatergic neurons. The GPe selectively inhibits caudal glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons, avoiding both cholinergic and rostral cells. This circuit characterization reveals non-canonical basal ganglia pathways for locomotion and valence.
Keywords: basal ganglia; brainstem; electrophysiology; inhibition; locomotion; mesencephalic locomotor region; optogenetics; pedunculopontine nucleus; reward; substantia nigra.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibitory basal ganglia nuclei differentially innervate pedunculopontine nucleus subpopulations and evoke differential motor and valence behaviors.Elife. 2025 Aug 20;13:RP102308. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102308. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40833252 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission of delta band (0.5-4 Hz) oscillations from the globus pallidus to the substantia nigra pars reticulata in dopamine depletion.J Comput Neurosci. 2022 Aug;51(3):361-380. doi: 10.1007/s10827-023-00853-z. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Comput Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 37266768 Free PMC article.
-
α4 nicotinic receptors on GABAergic neurons mediate a cholinergic analgesic circuit in the substantia nigra pars reticulata.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Jun;45(6):1160-1174. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01234-7. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38438581 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Lived Experience of Autistic Adults in Employment: A Systematic Search and Synthesis.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):495-509. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0114. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018061 Review.
References
-
- Wang H.-L., and Morales M. (2009). Pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei contain distinct populations of cholinergic, glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 29, 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06576.x. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06576.x. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
