This is a preprint.
Outcome of H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in calves and lactating cows
- PMID: 39149352
- PMCID: PMC11326275
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.08.09.607272
Outcome of H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in calves and lactating cows
Abstract
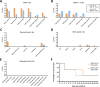
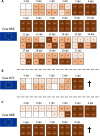
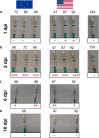
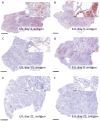
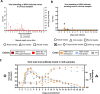
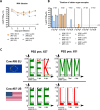
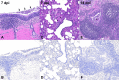
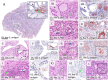
In March 2024, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) clade 2.3.4.4b H5N1 infections in dairy cows were first reported from Texas, USA. Rapid dissemination to more than 190 farms in 13 states followed. Here, we provide results of two independent clade 2.3.4.4b experimental infection studies evaluating (i) oronasal susceptibility and transmission in calves to a US H5N1 bovine isolate genotype B3.13 (H5N1 B3.13) and (ii) susceptibility of lactating cows following direct mammary gland inoculation of either H5N1 B3.13 or a current EU H5N1 wild bird isolate genotype euDG (H5N1 euDG). Inoculation of the calves resulted in moderate nasal replication and shedding with no severe clinical signs or transmission to sentinel calves. In dairy cows, infection resulted in no nasal shedding, but severe acute mammary gland infection with necrotizing mastitis and high fever was observed for both H5N1 genotypes/strains. Milk production was rapidly and drastically reduced and the physical condition of the cows was severely compromised. Virus titers in milk rapidly peaked at 108 TCID50/mL, but systemic infection did not ensue. Notably, adaptive mutation PB2 E627K emerged after intramammary replication of H5N1 euDG. Our data suggest that in addition to H5N1 B3.13, other HPAIV H5N1 strains have the potential to replicate in the udder of cows and that milk and milking procedures, rather than respiratory spread, are likely the primary routes of H5N1 transmission between cattle.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The J.A.R. laboratory received support from Tonix Pharmaceuticals, Genus plc, Xing Technologies, and Zoetis, outside of the reported work. J.A.R. is inventor on patents and patent applications on the use of antivirals and vaccines for the treatment and prevention of virus infections, owned by Kansas State University. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


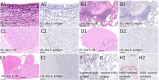

References
-
- (CDC), C. f. D. C. a. P. Technical Report: June 2023 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Viruses, <https://www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/php/technical-report/h5n1-070723.html?CDC_A...> (2023).
-
- (WHO), W. H. O. The panzootic spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 sublineage 2.3.4.4b: a critical appraisal of One Health preparedness and prevention, <https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/the-panzootic-spread-of-highly-p...> (2023). - PubMed
-
- Bevins S. N. et al. Intercontinental Movement of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4 Virus to the United States, 2021. Emerg Infect Dis 28, 1006–1011 (2022). https://doi.org:10.3201/eid2805.220318 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baechlein C. et al. Neurotropic Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus in Red Foxes, Northern Germany. Emerg Infect Dis 29, 2509–2512 (2023). https://doi.org:10.3201/eid2912.230938 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Plaza P. I., Gamarra-Toledo V., Rodriguez Eugui J., Rosciano N. & Lambertucci S. A. Pacific and Atlantic sea lion mortality caused by highly pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) in South America. Travel Med Infect Dis 59, 102712 (2024). https://doi.org:10.1016/j.tmaid.2024.102712 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
