The function of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitors in the development of disease
- PMID: 39149600
- PMCID: PMC11325723
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1432224
The function of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitors in the development of disease
Abstract
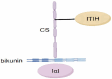
Through the formation of covalent connections with hyaluronic acid (HA), the inter-α-trypsin inhibitor (IαI) family collaborates to preserve the stability of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The five distinct homologous heavy chains (ITIH) and one type of light chain make up the IαI family. ITIH alone or in combination with bikunin (BK) has been proven to have important impacts in a number of earlier investigations. This implies that BK and ITIH might be crucial to both physiological and pathological processes. The functions of BK and ITIH in various pathophysiological processes are discussed independently in this paper. In the meanwhile, this study offers suggestions for further research on the roles of BK and ITIH in the course of disease and summarizes the plausible mechanisms of the previous studies.
Keywords: ITIHs; bikunin (BK); extracellular matrix (ECM); hyaluronic acid (HA); inter-α-trypsin inhibitor (IαI) family.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Zhang, Guo, Bai, Tian and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frequent expression loss of Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain (ITIH) genes in multiple human solid tumors: a systematic expression analysis.BMC Cancer. 2008 Jan 28;8:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-25. BMC Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18226209 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary bikunin determination provides insight into proteinase/proteinase inhibitor imbalance in patients with inflammatory diseases.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002 Jun;40(6):579-86. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2002.100. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2002. PMID: 12211652
-
The Biological Role of Hyaluronan-Rich Oocyte-Cumulus Extracellular Matrix in Female Reproduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 18;19(1):283. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010283. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29346283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inter-α-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 5 (ITIH5) is overexpressed in inflammatory skin diseases and affects epidermal morphology in constitutive knockout mice and murine 3D skin models.Exp Dermatol. 2015 Sep;24(9):663-8. doi: 10.1111/exd.12704. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25809190
-
Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor proteoglycan family--a group of proteins binding and stabilizing the extracellular matrix.Eur J Biochem. 1998 Mar 15;252(3):339-46. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2520339.x. Eur J Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9546647 Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal Proteomic Profiling of Cognition across an Aerobic Exercise Intervention.Ann Neurol. 2025 May;97(5):1007-1018. doi: 10.1002/ana.27210. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Ann Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40013367 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering New Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Through Proteomic and Network Analysis.Biology (Basel). 2025 Mar 4;14(3):256. doi: 10.3390/biology14030256. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136513 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Analysis of Inter-Alpha-Trypsin Inhibitor Heavy Chain 2 and Enolase 1 in Canine Mammary Tumors: Associations with Tumor Aggressiveness and Prognostic Significance.Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 2;12(2):110. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12020110. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40005870 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention of machine learning in bladder cancer research using multi-omics datasets: systematic review on biomarker identification.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 5;16(1):1010. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02734-6. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40471489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of stroke biomarkers using proteomic profiling of extracellular vesicles derived from human blood: a preliminary study.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 2;16:1587389. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1587389. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40672462 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

