Clinical presentation and factors associated with gluten exposure in children with celiac disease
- PMID: 39149789
- PMCID: PMC12070468
- DOI: 10.1002/jpn3.12321
Clinical presentation and factors associated with gluten exposure in children with celiac disease
Abstract
Objectives: The prevalence of celiac disease (CeD) is increasing, yet it is still underdiagnosed, in part because of its heterogeneous presentation. Diagnostic criteria are evolving and management with strict adherence to a gluten-free diet is challenging for many. We aimed to characterize the clinical presentation of CeD among a large multicenter cohort of pediatric patients and to identify factors associated with gluten-free diet adherence.
Methods: Patients with CeD aged 0-18 years were recruited from 11 United States health centers. Parents completed surveys about gluten-free diet adherence and patient electronic health records were reviewed. Logistic regression analyses were performed to identify risk factors associated with gluten exposure.
Results: Charts were reviewed for 460 children with a median age of 6.4 years. Abdominal pain was reported in 57% of the cohort, but diverse symptoms were identified. Parent surveys were completed for 455 participants. Sixty-five (14%) participants were at high risk for gluten exposure based on parental reports of weekly or daily gluten exposure or eating gluten by choice in the past year. Participants under the age of 5 years had a lower risk of gluten exposure, while participants without repeat serology testing 18 months after initial diagnosis were at higher risk of gluten exposure.
Conclusions: In a large, multicenter cohort of pediatric CeD patients, clinical presentation is highly variable, necessitating a high index of suspicion to make a diagnosis. Parent surveys indicate that 14% of patients are at high risk of gluten exposure, with patient age and lack of close follow-up associated with gluten-free diet adherence.
Keywords: epidemiology; self‐management; treatment adherence and compliance.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition.
Figures

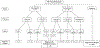
References
-
- Singh P, Arora A, Strand TA, et al. Global Prevalence of Celiac Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. 2018;16(6):823–836 e822. - PubMed
-
- Lebwohl B, Rubio-Tapia A. Epidemiology, Presentation, and Diagnosis of Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(1):63–75. - PubMed
-
- Makharia GK, Singh P, Catassi C, et al. The global burden of coeliac disease: opportunities and challenges. Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2022;19(5):313–327. - PubMed
-
- Husby S, Koletzko S, Korponay-Szabó I, et al. European Society Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Guidelines for Diagnosing Coeliac Disease 2020. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition. 2020;70(1):141–156. - PubMed
-
- Hill ID, Fasano A, Guandalini S, et al. NASPGHAN Clinical Report on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gluten-related Disorders. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition. 2016;63(1):156–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 DK119584/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK122127/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23DK119584(JAS)/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health
- K23DK122127(MML)/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

