Improved sub-genomic RNA prediction with the ARTIC protocol
- PMID: 39149898
- PMCID: PMC11417393
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae687
Improved sub-genomic RNA prediction with the ARTIC protocol
Abstract
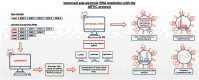
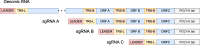
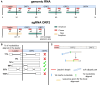
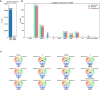
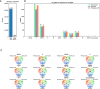
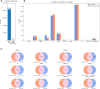
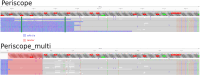
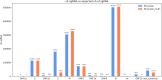
Viral subgenomic RNA (sgRNA) plays a major role in SARS-COV2's replication, pathogenicity, and evolution. Recent sequencing protocols, such as the ARTIC protocol, have been established. However, due to the viral-specific biological processes, analyzing sgRNA through viral-specific read sequencing data is a computational challenge. Current methods rely on computational tools designed for eukaryote genomes, resulting in a gap in the tools designed specifically for sgRNA detection. To address this, we make two contributions. Firstly, we present sgENERATE, an evaluation pipeline to study the accuracy and efficacy of sgRNA detection tools using the popular ARTIC sequencing protocol. Using sgENERATE, we evaluate periscope, a recently introduced tool that detects sgRNA from ARTIC sequencing data. We find that periscope has biased predictions and high computational costs. Secondly, using the information produced from sgENERATE, we redesign the algorithm in periscope to use multiple references from canonical sgRNAs to mitigate alignment issues and improve sgRNA and non-canonical sgRNA detection. We evaluate periscope and our algorithm, periscope_multi, on simulated and biological sequencing datasets and demonstrate periscope_multi's enhanced sgRNA detection accuracy. Our contribution advances tools for studying viral sgRNA, paving the way for more accurate and efficient analyses in the context of viral RNA discovery.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Lamers M.M., Haagmans B.L.. SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022; 20:270–284. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

