Coronary computed tomography angiography improves assessment of patients with acute chest pain and inconclusively elevated high-sensitivity troponins
- PMID: 39150488
- PMCID: PMC11782329
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-024-10930-1
Coronary computed tomography angiography improves assessment of patients with acute chest pain and inconclusively elevated high-sensitivity troponins
Abstract
Objectives: To determine whether coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) can improve the diagnostic work-up of patients with acute chest pain and inconclusively high-sensitivity troponins (hs-troponin).
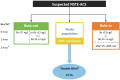
Methods: We conducted a prospective, blinded, observational, multicentre study. Patients aged 30-80 years presenting to the emergency department with acute chest pain and inconclusively elevated hs-troponins were included and underwent CCTA. The primary outcome was the diagnostic accuracy of ≥ 50% stenosis on CCTA to identify patients with type-1 non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS).
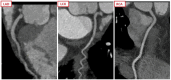
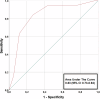
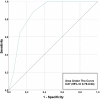
Results: A total of 106 patients (mean age 65 ± 10, 29% women) were enrolled of whom 20 patients (19%) had an adjudicated diagnosis of type-1 NSTE-ACS. In 45 patients, CCTA revealed non-obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) or no CAD. Sensitivity, specificity, negative predictive value (NPV), positive predictive value and area-under-the-curve (AUC) of ≥ 50% stenosis on CCTA to identify patients with type 1 NSTE-ACS, was 95% (95% confidence interval: 74-100), 56% (45-68), 98% (87-100), 35% (29-41) and 0.83 (0.73-0.94), respectively. When only coronary segments with a diameter ≥ 2 mm were considered for the adjudication of type 1 NSTE-ACS, the sensitivity and NPV increased to 100%. In 8 patients, CCTA enabled the detection of clinically relevant non-coronary findings.
Conclusion: The absence of ≥ 50% coronary artery stenosis on CCTA can be used to rule out type 1 NSTE-ACS in acute chest pain patients with inconclusively elevated hs-troponins. Additionally, CCTA can help improve the diagnostic work-up by detecting other relevant conditions that cause acute chest pain and inconclusively elevated hs-troponins.
Clinical relevance statement: Coronary CTA (CCTA) can safely rule out type 1 non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) in patients presenting to the ED with acute chest pain and inconclusively elevated hs-troponins, while also detecting other relevant non-coronary conditions.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03129659). Registered on 26 April 2017 KEY POINTS: Acute chest discomfort is a common presenting complaint in the emergency department. CCTA achieved very high negative predictive values for type 1 NSTE-ACS in this population. CCTA can serve as an adjunct for evaluating equivocal ACS and evaluates for other pathology.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Computed tomography angiography; Non-ST elevated myocardial infarction; Troponin.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards. Guarantor: The scientific guarantor of this publication is Eric A. Dubois. Conflict of interest: The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. Statistics and biometry: No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Informed consent: Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Ethical approval: Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Study subjects or cohorts overlap: NA Methodology: Prospective Observational Multicentre study
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coronary CT angiography for improved assessment of patients with acute chest pain and low-range positive high-sensitivity troponins: study protocol for a prospective, observational, multicentre study (COURSE trial).BMJ Open. 2021 Oct 18;11(10):e049349. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049349. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34663657 Free PMC article.
-
Coronary CT Angiography for Suspected ACS in the Era of High-Sensitivity Troponins: Randomized Multicenter Study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Jan 5;67(1):16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.10.045. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26764061 Clinical Trial.
-
CCTA in patients with positive troponin and low clinical suspicion for ACS: a useful diagnostic option to exclude obstructive CAD.Emerg Radiol. 2019 Jun;26(3):269-275. doi: 10.1007/s10140-019-01668-1. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Emerg Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30631994
-
The role of coronary CT angiography for acute chest pain in the era of high-sensitivity troponins.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2019 Sep-Oct;13(5):267-273. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2019.05.007. Epub 2019 Jun 15. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2019. PMID: 31235403 Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of functional, imaging and biochemical tests for patients presenting with chest pain to the emergency department: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2019 Aug;8(5):412-420. doi: 10.1177/2048872617754275. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2019. PMID: 29350536
Cited by
-
Computed tomography angiography in the diagnosis of non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: redefining our first line of defense.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2025 May 2;59:101690. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2025.101690. eCollection 2025 Aug. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2025. PMID: 40453066 Free PMC article.
-
Value of upfront coronary computed tomography angiography in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025 Apr;41(4):733-742. doi: 10.1007/s10554-025-03360-7. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40045073
References
-
- Collet JP, Thiele H, Barbato E et al (2020) 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J 42:1289–1367 - PubMed
-
- Mueller C, Giannitsis E, Christ M et al (2016) Multicenter evaluation of a 0-hour/1-hour algorithm in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction with high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T. Ann Emerg Med 68:76–87.e74 - PubMed
-
- Nestelberger T, Wildi K, Boeddinghaus J et al (2016) Characterization of the observe zone of the ESC 2015 high-sensitivity cardiac troponin 0h/1h-algorithm for the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 207:238–245 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

