Characterization of the vaginal microbiota in Italian women with endometriosis: preliminary study
- PMID: 39150504
- PMCID: PMC11393154
- DOI: 10.1007/s00404-024-07631-x
Characterization of the vaginal microbiota in Italian women with endometriosis: preliminary study
Abstract
Purpose: This cross-sectional study aims to assess the interplay between the vaginal microbiota and endometriosis.
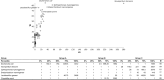
Methods: 123 consecutive Italian fertile women, aged between 20 and 40 years old, were enrolled during a routine gynecological consultation; 24 were diagnosed with endometriosis and 99 did not complain of any gynecological disease. All women underwent a vaginal swab for the evaluation of the composition and diversity of vaginal microbiota by means of 16 s rDNA metagenomic sequencing.
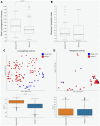
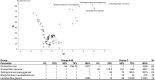
Results: Compared to women with no gynecological disease, the vaginal microbiota in women with endometriosis showed a similar abundance of Lactobacillus spp.; however, a statistically significant lower abundance in the genera Pseudomonas (p < 0.01), Bifidobacterium (p < 0.05), Novispirillum (p < 0.0000001) and Sphingomonas (p < 0.0000001), and a statistically significant increase in the abundance of the genera Escherichia (p < 0.00001), Megasphaera (p < 0.00001), and Sneathia (p < 0.0001) were observed.
Conclusions: There is a complex interplay between vaginal microbiota composition and endometriosis, showing a distinct microbial signature in the bacterial genera usually found in dysbiosis.
Keywords: Dysbiosis; Endometriosis; Metagenomic analysis; Vaginal microbiota.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Giuliani M, Cosmi V, Pierleoni L, Recine A, Pieroni M, Ticino A, Porpora MG, Simonelli C (2016) Quality of life and sexual satisfaction in women suffering from endometriosis: an Italian preliminary study. Sexologies 25(1):e12–e19 10.1016/j.sexol.2015.03.004 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

