The humanized platelet glycoprotein VI Fab inhibitor EMA601 protects from arterial thrombosis and ischaemic stroke in mice
- PMID: 39150906
- PMCID: PMC11560278
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae482
The humanized platelet glycoprotein VI Fab inhibitor EMA601 protects from arterial thrombosis and ischaemic stroke in mice
Abstract
Background and aims: Glycoprotein VI (GPVI) is a platelet collagen/fibrin(ogen) receptor and an emerging pharmacological target for the treatment of thrombotic and thrombo-inflammatory diseases, notably ischaemic stroke. A first anti-human GPVI (hGPVI) antibody Fab-fragment (ACT017/glenzocimab, KD: 4.1 nM) recently passed a clinical phase 1b/2a study in patients with acute ischaemic stroke and was found to be well tolerated, safe, and potentially beneficial. In this study, a novel humanized anti-GPVI antibody Fab-fragment (EMA601; KD: 0.195 nM) was developed that inhibits hGPVI function with very high potency in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: Fab-fragments of the mouse anti-hGPVI IgG Emf6.1 were tested for functional GPVI inhibition in human platelets and in hGPVI expressing (hGP6tg/tg) mouse platelets. The in vivo effect of Emf6.1Fab was assessed in a tail bleeding assay, an arterial thrombosis model and the transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) model of ischaemic stroke. Using complementary-determining region grafting, a humanized version of Emf6.1Fab (EMA601) was generated. Emf6.1Fab/EMA601 interaction with hGPVI was mapped in array format and kinetics and quantified by bio-layer interferometry.
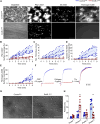
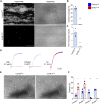
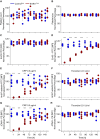
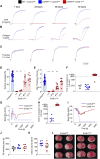
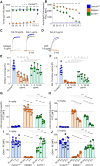
Results: Emf6.1Fab (KD: 0.427 nM) blocked GPVI function in human and hGP6tg/tg mouse platelets in multiple assays in vitro at concentrations ≥5 µg/mL. Emf6.1Fab (4 mg/kg)-treated hGP6tg/tg mice showed potent hGPVI inhibition ex vivo and were profoundly protected from arterial thrombosis as well as from cerebral infarct growth after tMCAO, whereas tail-bleeding times remained unaffected. Emf6.1Fab binds to a so far undescribed membrane proximal epitope in GPVI. The humanized variant EMA601 displayed further increased affinity for hGPVI (KD: 0.195 nM) and fully inhibited the receptor at 0.5 µg/mL, corresponding to a >50-fold potency compared with ACT017.
Conclusions: EMA601 is a conceptually novel and promising anti-platelet agent to efficiently prevent or treat arterial thrombosis and thrombo-inflammatory pathologies in humans at risk.
Keywords: Anti-platelet therapy; GPVI; Platelet; Stroke; Thrombosis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures



References
-
- Michelson AD, Cattaneo M, Frelinger A, Newman P. Platelets. 4th edn. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier; 2019.
-
- Stellos K, Bigalke B, Borst O, Pfaff F, Elskamp A, Sachsenmaier S, et al. Circulating platelet-progenitor cell coaggregate formation is increased in patients with acute coronary syndromes and augments recruitment of CD34+ cells in the ischaemic microcirculation. Eur Heart J 2013;34:2548–56. 10.1093/eurheartj/eht131 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

