Challenges of Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Osteopetrosis
- PMID: 39151178
- PMCID: PMC11421562
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-23-01208
Challenges of Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Osteopetrosis
Abstract
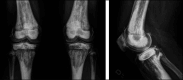
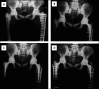
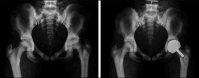
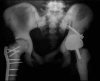
Osteopetrosis is a rare metabolic bone disease, characterized by dysfunction of osteoclasts, resulting in increased bone density and brittleness leading to pathological fractures and bone deformities. Hip and knee osteoarthritis (OA) are common long-term complications in patients with osteopetrosis. Joint arthroplasty surgery remains an effective and recommended treatment for these patients with an end-stage OA because it provides favorable outcomes. However, in osteopetrosis, joint arthroplasty surgery carries an increased risk of complications, and specific preoperative and perioperative considerations are required to deal with the technical challenges related to the disease. The aim of this article was to review some of the key aspects of osteopetrosis, provide technical recommendations, and answer clinically relevant questions related to hip and knee arthroplasty surgery.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the following authors or any immediate family member has received anything of value from or has stock or stock options held in a commercial company or institution related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article: Dr. Beckers, Dr. Mazy, Dr. Vendittoli, Dr. Morcos, and Dr. Massé
Figures

References
-
- Shapiro F: Osteopetrosis. Current clinical considerations. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;294:34-44. - PubMed
-
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP: Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am Vol 2018;100:1455-1460. - PubMed
-
- Krzysztof H, Wlodarski MD: Properties and origin of osteoblasts. Clin Orthop 1990;252:276-289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

