Reduced plasma interleukin-6 concentration after transcranial direct current stimulation to the prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 39151649
- PMCID: PMC11401619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115201
Reduced plasma interleukin-6 concentration after transcranial direct current stimulation to the prefrontal cortex
Abstract
Objectives: Transcranial direct stimulation (tDCS) targeted to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) reduces food intake and hunger, but its effects on circulating factors are unclear. We assessed the effect of repeated administration of tDCS to the left DLPFC (L-DLPFC) on concentrations of pro/anti-inflammatory and appetitive hormone concentrations.
Materials and methods: Twenty-nine healthy adults with obesity (12 M; 42±11 y; BMI=39±8 kg/m2) received 3 consecutive inpatient sessions of either anodal or sham tDCS targeted to the L-DLPFC during a period of ad libitum food intake. Fasting plasma concentrations of IL-6, orexin, cortisol, TNF-α, IL-1β, ghrelin, PYY, and GLP-1 were measured before the initial and after the final tDCS sessions.
Results: IL-6 (β=-0.92 pg/ml p=0.03) decreased in the anodal group compared with sham, even after adjusting for kcal intake; there were no changes in other hormones. Mean kcal intake was associated with higher IL-1β and ghrelin concentrations after the ad libitum period (β=0.00018 pg/ml/kcal, p=0.03; β=0.00011 pg/ml/kcal, p=0.02; respectively), but not differ by intervention groups.
Conclusions: IL-6 concentrations were reduced following anodal tDCS to the L-DLPFC independent of ad libitum intake. IL-6 concentrations reflect the inflammatory state of adiposity and may affect eating behavior and weight gain. These findings provide evidence of therapeutic benefit of tDCS.
Keywords: Appetitive hormones; Cytokines; Food intake; Inflammation; Non-Invasive Neuromodulation; Obesity; Pro-inflammatory hormones.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures
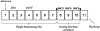

References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN, Farzadfar F, Riley LM, Ezzati M, Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating G, National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants, Lancet 377(9765) (2011) 557–67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hales CM, National Center for Health S, Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, Hyattsville, MD, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

