Motor innervation directs the correct development of the mouse sympathetic nervous system
- PMID: 39152112
- PMCID: PMC11329663
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51290-0
Motor innervation directs the correct development of the mouse sympathetic nervous system
Abstract
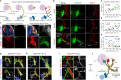
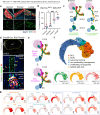
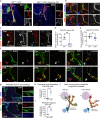
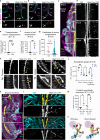
The sympathetic nervous system controls bodily functions including vascular tone, cardiac rhythm, and the "fight-or-flight response". Sympathetic chain ganglia develop in parallel with preganglionic motor nerves extending from the neural tube, raising the question of whether axon targeting contributes to sympathetic chain formation. Using nerve-selective genetic ablations and lineage tracing in mouse, we reveal that motor nerve-associated Schwann cell precursors (SCPs) contribute sympathetic neurons and satellite glia after the initial seeding of sympathetic ganglia by neural crest. Motor nerve ablation causes mispositioning of SCP-derived sympathoblasts as well as sympathetic chain hypoplasia and fragmentation. Sympathetic neurons in motor-ablated embryos project precociously and abnormally towards dorsal root ganglia, eventually resulting in fusion of sympathetic and sensory ganglia. Cell interaction analysis identifies semaphorins as potential motor nerve-derived signaling molecules regulating sympathoblast positioning and outgrowth. Overall, central innervation functions both as infrastructure and regulatory niche to ensure the integrity of peripheral ganglia morphogenesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wehrwein, E. A., Orer, H. S. & Barman, S. M. Overview of the anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology of the autonomic nervous system. Compr. Physiol. 6, 1239–1278 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- F32 DE029662/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- STEMMING-FROM-NERVE/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- Career Development Award/Giovanni Armenise-Harvard Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

