The Fanconi anemia core complex promotes CtIP-dependent end resection to drive homologous recombination at DNA double-strand breaks
- PMID: 39152113
- PMCID: PMC11329772
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51090-6
The Fanconi anemia core complex promotes CtIP-dependent end resection to drive homologous recombination at DNA double-strand breaks
Abstract
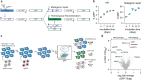
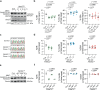
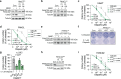
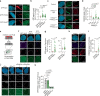
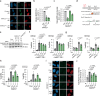
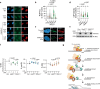
During the repair of interstrand crosslinks (ICLs) a DNA double-strand break (DSB) is generated. The Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex, which is recruited to ICLs, promotes high-fidelity repair of this DSB by homologous recombination (HR). However, whether the FA core complex also promotes HR at ICL-independent DSBs, for example induced by ionizing irradiation or nucleases, remains controversial. Here, we identified the FA core complex members FANCL and Ube2T as HR-promoting factors in a CRISPR/Cas9-based screen. Using isogenic cell line models, we further demonstrated an HR-promoting function of FANCL and Ube2T, and of their ubiquitination substrate FANCD2. We show that FANCL and Ube2T localize at DSBs in a FANCM-dependent manner, and are required for the DSB accumulation of FANCD2. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that FANCL ubiquitin ligase activity is required for the accumulation of CtIP at DSBs, thereby promoting end resection and Rad51 loading. Together, these data demonstrate a dual genome maintenance function of the FA core complex and FANCD2 in promoting repair of both ICLs and DSBs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
The Fanconi anemia core complex promotes CtIP-dependent end-resection to drive homologous recombination at DNA double-strand breaks.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 6:2023.09.05.556391. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.05.556391. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 16;15(1):7076. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51090-6. PMID: 37732274 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C42454/A28596/Cancer Research UK (CRUK)
- VI.C.182.052/Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research)
- C9685/A26398/Cancer Research UK (CRUK)
- 310030_197003/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- P30 CA014051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ERC-CoG-617485/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- P30 ES002109/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-ES015339/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 CA226898/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35-ES028374/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- C9545/A29580/Cancer Research UK (CRUK)
- BUIT 2015-7546/KWF Kankerbestrijding (Dutch Cancer Society)
- R01 ES015339/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA226898/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P30-CA14051/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R35 ES028374/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

