Effect of arginine, glycine + serine concentrations, and guanidinoacetic acid supplementation in vegetable-based diets for chickens
- PMID: 39153445
- PMCID: PMC11378898
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104105
Effect of arginine, glycine + serine concentrations, and guanidinoacetic acid supplementation in vegetable-based diets for chickens
Abstract
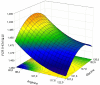
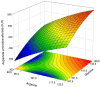
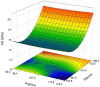
The study investigated guanidinoacetic acid (GAA) supplementation with varying dietary digestible arginine (Arg) and glycine+serine (Gly+Ser) concentrations in the starter phase, exploring respective carry-over effects on growth performance, blood chemistry, incidence of pectoral myopathies and proximate composition in broilers. A total of 2,800 one-day-old male broiler chicks were distributed in a central composite design with 2 factors and double experimental mesh, represented by supplementation or omission of 0.6 g per kg of GAA, with a central point represented by 107% of Arg and 147% of Gly+Ser, 4 factorial points (combinations of Arg/Gly+Ser concentrations: 96.4/132.5%; 117.6/132.5%; 96.4/161.5%, and 117.6/132.5%), and 4 axial points (combinations of axial points estimated for Arg and Gly+Ser, with the central points of 92/147%; 122/147%; 107/126.5, and 107/167.5%), totaling 18 treatments, 4 repetitions to factorial and axial points, 24 replicates to the central point, and 25 birds per pen. Feed conversion ratio (FCR) from d 1 to 10 had a linear response (P = 0.009) for the decreasing Arg content and a quadratic response (P = 0.047) for Gly+Ser concentrations. Broilers supplemented GAA had lower FCR compared with nonsupplemented groups from d 1 to 10 (P = 0.048) and d 1 to 42 (P = 0.026). Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) exhibited increasing and decreasing linear effects as a function of Arg (P = 0.008) and Gly+Ser (P = 0.020) concentrations, respectively. Guanidinoacetic acid decreased serum AST (P = 0.028). Guanidinoacetic acid reduced moderate + severe (P = 0.039) and mild (P = 0.015) Wooden Breast scores. The occurrence of normal White Striping increased (P = 0.002), while severe score was reduced (P = 0.029) with GAA supplementation. In conclusion, increased digestible Arg:Lys and 14% and 6% above the recommendations (107% and 147%), respectively, provided improved FCR during the starter phase. Dietary GAA supplementation (0.6 g per kg) improved FCR, reduced severity of breast myopathies and appears to have reduced muscle damage in broilers fed plant-based diets.
Keywords: amino acid; creatine; muscular dystrophy; white striping; wooden breast.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Adeva M.M., Souto G., Blanco N., Donapetry C. Ammonium metabolism in humans. Metabolism. 2012;61:1495–1511. - PubMed
-
- Ale Saheb Fosoul S., Azarfar A., Gheisari A., Khosravinia H. Utilização de energia de frangos de corte em resposta à suplementação de ácido guanidinoacético em dietas com diversos conteúdos energéticos. Br. J. Nutr. 2018;120:131–140. - PubMed
-
- Association of Official . Analytical Chemists - AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. 17th ed. AOAC Int; Gaithersburg: MD: 2000.
Further readings
-
- Abudabos A.M., Saleh F., Lemme A., Zakaria H.A.H. The relationship between guanidino acetic acid and metabolisable energy concentration of diets on performance of broiler chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2014;13:3269.
-
- Aviagen . Ross broiler pocket guide: the pocket guide. 2015.
-
- Dilger R.N., Bryant-Angeoni K., Payne R.L., Lemme A., Parsons C.M. Dietary guanidino acetic acid is an efficacious replacement for arginine for young chicks Poult. Sci. 2013:171–177. - PubMed
-
- Esser A.F.G. Effects of guanidionoacetic acid and arginine supplementation to vegetable diets fed to broiler chickens subjected to heat stress before slaughter. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2017;19:429–436.
-
- Fernandes J.I.M., Murakami A.E., Martins E.N., Sakamoto M.I., Garcia E.R. Effect of arginine on the development of the pectoralis muscle and the diameter and the protein: deoxyribonucleicacid rate of its skeletal myofibers in broilers Poult. Sci. 2009:1399–1406. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

