Nuclear PKM2 binds pre-mRNA at folded G-quadruplexes and reveals their gene regulatory role
- PMID: 39153475
- PMCID: PMC11455610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.07.025
Nuclear PKM2 binds pre-mRNA at folded G-quadruplexes and reveals their gene regulatory role
Abstract
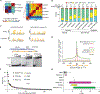
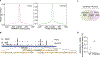
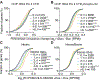
Nuclear localization of the metabolic enzyme PKM2 is widely observed in various cancer types. We identify nuclear PKM2 as a non-canonical RNA-binding protein (RBP) that specifically interacts with folded RNA G-quadruplex (rG4) structures in precursor mRNAs (pre-mRNAs). PKM2 occupancy at rG4s prevents the binding of repressive RBPs, such as HNRNPF, and promotes the expression of rG4-containing pre-mRNAs (the "rG4ome"). We observe an upregulation of the rG4ome during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and a negative correlation of rG4 abundance with patient survival in different cancer types. By preventing the nuclear accumulation of PKM2, we could repress the rG4ome in triple-negative breast cancer cells and reduce migration and invasion of cancer cells in vitro and in xenograft mouse models. Our data suggest that the balance of folded and unfolded rG4s controlled by RBPs impacts gene expression during tumor progression.
Keywords: G-quadruplex; G4; PAR-CLIP; PKM2; RNA-binding proteins; crosslinking and immunoprecipitation; posttranscriptional gene regulation.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.R. is on the scientific advisory board and has an equity interest in Pearl Bio. J.R. is a co-founder and has an equity interest in Kapis Biosciences.
Figures


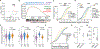

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

