Cytosolic calcium regulates hepatic mitochondrial oxidation, intrahepatic lipolysis, and gluconeogenesis via CAMKII activation
- PMID: 39153480
- PMCID: PMC11446666
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.07.016
Cytosolic calcium regulates hepatic mitochondrial oxidation, intrahepatic lipolysis, and gluconeogenesis via CAMKII activation
Abstract
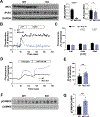
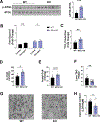
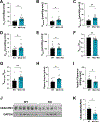
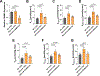
To examine the roles of mitochondrial calcium Ca2+ ([Ca2+]mt) and cytosolic Ca2+ ([Ca2+]cyt) in the regulation of hepatic mitochondrial fat oxidation, we studied a liver-specific mitochondrial calcium uniporter knockout (MCU KO) mouse model with reduced [Ca2+]mt and increased [Ca2+]cyt content. Despite decreased [Ca2+]mt, deletion of hepatic MCU increased rates of isocitrate dehydrogenase flux, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase flux, and succinate dehydrogenase flux in vivo. Rates of [14C16]palmitate oxidation and intrahepatic lipolysis were increased in MCU KO liver slices, which led to decreased hepatic triacylglycerol content. These effects were recapitulated with activation of CAMKII and abrogated with CAMKII knockdown, demonstrating that [Ca2+]cyt activation of CAMKII may be the primary mechanism by which MCU deletion promotes increased hepatic mitochondrial oxidation. Together, these data demonstrate that hepatic mitochondrial oxidation can be dissociated from [Ca2+]mt and reveal a key role for [Ca2+]cyt in the regulation of hepatic fat mitochondrial oxidation, intrahepatic lipolysis, gluconeogenesis, and lipid accumulation.
Keywords: CAMKII; Q-Flux; calcium; fat oxidation; glucose oxidation; isocitrate dehydrogenase flux; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; mitochondria; mitochondrial calcium uniporter; succinate dehydrogenase flux; tricarboxylic acid cycle; type 2 diabetes; α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase flux.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
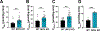
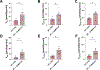

References
-
- Linn TC, Pettit FH, and Reed LJ (1969). α-KETO ACID DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEXES, X. REGULATION OF THE ACTIVITY OF THE PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX FROM BEEF KIDNEY MITOCHONDRIA BY PHOSPHORYLATION AND DEPHOSPHORYLATION*. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 62, 234–241. 10.1073/pnas.62.1.234. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK113984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007356/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK135645/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119968/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DK120534/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK131846/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK126362/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133143/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM136651/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007324/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA028765/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK116774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR071942/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

