MicroRNA-455-3P as a peripheral biomarker and therapeutic target for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39153602
- PMCID: PMC11383742
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102459
MicroRNA-455-3P as a peripheral biomarker and therapeutic target for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
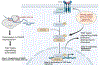
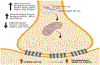
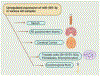
MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNAs evolutionary conserved molecules. They regulate cellular processes, including RNA silencing, post-translational gene expression and neurodegeneration. MicroRNAs are involved with human diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease (AD) and others. Interestingly, cerebrospinal fluids (CSF) and the blood of AD patients have altered expressions of many RNAs, which may serve as potential peripheral biomarkers. The intensive investigation from our lab revealed that microRNA-455-3 P (miR-455-3p) is a strong candidate as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for AD. Several genes implicated in the pathogenesis of AD are directly targeted by miR-455-3p. Several years of our lab research revealed that miR-455-3p regulates important physiological processes associated with AD, such as the processing of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), TGF-β signaling, the regulation of oxidative stress, mitochondrial biogenesis, and synaptic damages. The expression of miR-455-3p in mild cognitive impaired subjects and AD patients pointed out its involvement in AD progression. Recently, our lab generated both transgenic and knockout mice for miR-455-3p. Interestingly miR-455-3p transgenic mice showed superior cognitive learning, improved memory and extended lifespan compared to age matched wild-type mice, whereas miR-455-3-p knockout mice showed cognitive decline and reduced lifespan. Information derived from mouse models further demonstrated the advantageous impact of miR-455-3p on dendritic growth, synaptogenesis, and mitochondrial biogenesis in preventing the onset and progression of AD. The identification of miR-455-3p as a biomarker was suggested by its presence in postmortem AD brains, B-lymphocytes, and fibroblasts. Our hypothesis that miR-455-3p could be a peripheral biomarker and therapeutic target for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid precursor protein; Biomarker; Cognitive behavior; MicroRNA-455–3-p; Mitochondria; Synaptogenesis.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

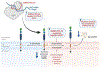

Similar articles
-
A New Discovery of MicroRNA-455-3p in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(s1):S117-S130. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190583. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 31524168 Review.
-
MicroRNA-455-3p as a potential peripheral biomarker for Alzheimer's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Oct 1;26(19):3808-3822. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx267. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28934394 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Expression of microRNA-1273g-3p Contributes to Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis by Regulating the Expression of Mitochondrial Genes.Cells. 2021 Oct 9;10(10):2697. doi: 10.3390/cells10102697. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685681 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression of miR-34a induces rapid cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease-like pathology.Brain Res. 2019 Oct 15;1721:146327. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146327. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31295467 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-323-3p with clinical potential in rheumatoid arthritis, Alzheimer's disease and ectopic pregnancy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Feb;18(2):153-8. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.855201. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 24283221 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological Function Analysis of MicroRNAs and Proteins in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 10;25(24):13260. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413260. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell culture research in aging and Alzheimer's disease: The strategic use/reuse of untreated controls and savings people's tax dollars.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025 Jan 15;9:25424823241310716. doi: 10.1177/25424823241310716. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025. PMID: 40034533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in Regulating miRNAs for Biomarkers of Neurodegenerative Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;62(6):7576-7596. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04733-8. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39918711 Review.
-
miRNA mediated mitochondrial function and gene regulation associated with Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging. 2025 May 13;6:1582812. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1582812. eCollection 2025. Front Aging. 2025. PMID: 40433169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the Role of ESR1 in Breast Cancer: Correlation with microRNA, lncRNA, and Methylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 27;26(7):3101. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073101. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amaral PP, Dinger ME, Mercer TR, Mattick JS, 2008. The eukaryotic genome as an RNA machine. science 319, 1787–1789. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V, 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431, 350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP, 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. cell 116, 281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

