Multimodal MRI-based deep-radiomics model predicts response in cervical cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
- PMID: 39154103
- PMCID: PMC11330439
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-70055-9
Multimodal MRI-based deep-radiomics model predicts response in cervical cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
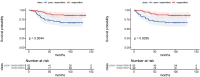
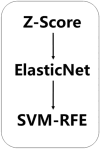
Platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) followed by radical hysterectomy has been proposed as an alternative treatment approach for cervical cancer (CC) in stage Ib2-IIb, who had a strong desire to be treated with surgery. Our study aims to develop a model based on multimodal MRI by using radiomics and deep learning to predict the treatment response in CC patients treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NACRT). From August 2009 to June 2013, CC patients in stage Ib2-IIb (FIGO 2008) who received NACRT at Fujian Cancer Hospital were enrolled in our study. Clinical information, contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging (CE-T1WI), and T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) data were respectively collected. Radiomic features and deep abstract features were extracted from the images using radiomics and deep learning models, respectively. Then, ElasticNet and SVM-RFE were employed for feature selection to construct four single-sequence feature sets. Early fusion of two multi-sequence feature sets and one hybrid feature set were performed, followed by classification prediction using four machine learning classifiers. Subsequently, the performance of the models in predicting the response to NACRT was evaluated by separating patients into training and validation sets. Additionally, overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were assessed using Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Among the four machine learning models, SVM exhibited the best predictive performance (AUC=0.86). Among the seven feature sets, the hybrid feature set achieved the highest values for AUC (0.86), ACC (0.75), Recall (0.75), Precision (0.81), and F1-score (0.75) in the validation set, outperforming other feature sets. Furthermore, the predicted outcomes of the model were closely associated with patient OS and DFS (p = 0.0044; p = 0.0039). A model based on MRI images with features from multiple sequences and different methods could precisely predict the response to NACRT in CC patients. This model could assist clinicians in devising personalized treatment plans and predicting patient survival outcomes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures