Safflower Alleviates Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension by Inactivating NLRP3: A Combined Approach of Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification
- PMID: 39155275
- PMCID: PMC11330698
- DOI: 10.1111/crj.13826
Safflower Alleviates Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension by Inactivating NLRP3: A Combined Approach of Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification
Abstract
Introduction: Traditional Chinese medicinal plant, safflower, shows effective for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), yet the underlying mechanisms remain largely unexplored. This study is aimed at exploring the potential molecular mechanisms of safflower in the treatment of PAH.
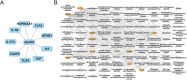
Methods: Network pharmacology approach and molecular docking were applied to identify the core active compounds, therapeutic targets, and potential signaling pathways of safflower against PAH. Meanwhile, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) assay was performed to determine the core compounds from safflower. Further, the mechanism of action of safflower on PAH was verified by in vivo and in vitro experiments.
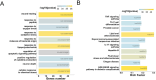
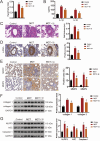
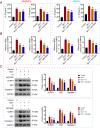
Results: A total of 15 active compounds and 177 targets were screened from safflower against PAH. Enrichment analysis indicated that these therapeutic targets were mainly involved in multiple key pathways, such as TNF signaling pathway and Th17 cell differentiation. Notably, molecular docking revealed that quercetin (core compound in safflower) displayed highest binding capacity with NLRP3. In vivo, safflower exerted therapeutic effects on PAH by inhibiting right ventricular hypertrophy, inflammatory factor release, and pulmonary vascular remodeling. Mechanistically, it significantly reduced the expression of proangiogenesis-related factors (MMP-2, MMP-9, Collagen 1, and Collagen 3) and NLRP3 inflammasome components (NLRP3, ASC, and Caspase-1) in PAH model. Similarly, these results were observed in vitro. Besides, we further confirmed that NLRP3 inhibitor had the same therapeutic effect as safflower in vitro.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that safflower mitigates PAH primarily by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. This provides novel insights into the potential use of safflower as an alternative therapeutic approach for PAH.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammation; network pharmacology; pulmonary arterial hypertension; quercetin; safflower.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Clinical Respiratory Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Cardioprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Astragalus-Safflower Herb Pairs on Coronary Heart Disease Identified by Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 May 22;28(5):94. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2805094. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37258471
-
Safflower injection inhibits pulmonary arterial remodeling in a monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rat model.Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2020 Dec 2;76(1-2):27-34. doi: 10.1515/znc-2020-0004. Print 2021 Jan 27. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33725750
-
Hydroxy-Safflower Yellow A Mitigates Vascular Remodeling in Rat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Feb 20;18:475-491. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S439686. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38405578 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of peach kernel and safflower herb-pair for the treatment of liver fibrosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Apr 21;102(16):e33593. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033593. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37083803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic targets for pulmonary arterial hypertension: insights into the emerging landscape.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2025 Jun;29(6):327-343. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2025.2507034. Epub 2025 May 21. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2025. PMID: 40368635 Review.
Cited by
-
[Application of Animal Models in Research on Hypoxia-Related Diseases].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Mar 20;56(2):331-338. doi: 10.12182/20250360101. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40599265 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Regulation of the Pulmonary Vasculature in Health and Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 14;14(3):341. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030341. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227402 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Luna‐López R., Ruiz Martín A., and Escribano Subías P., “Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension,” Medicina Clínica 158, no. 12 (2022): 622–629. - PubMed
-
- Dai Y., Chen X., Song X., et al., “Immunotherapy of Endothelin‐1 Receptor Type A for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension,” Journal of the American College of Cardiology 73, no. 20 (2019): 2567–2580. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

