Pleomorphic adenoma and carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma tumorigenesis: A proteomic analysis
- PMID: 39155517
- PMCID: PMC12021308
- DOI: 10.1111/odi.15109
Pleomorphic adenoma and carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma tumorigenesis: A proteomic analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To conduct a comprehensive proteomic analysis of normal salivary gland tissue, pleomorphic adenoma (PA), and carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma (CXPA), and validate the proteomic findings using immunohistochemistry.
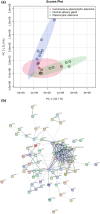
Methods: Six normal salivary gland tissues, seven PA and seven CXPA samples underwent laser microdissection followed by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Protein identification and quantification were performed using MaxQuant software. Statistical analysis and functional enrichment were conducted using the Perseus platform and STRING tool, respectively. Immunohistochemistry was used for validation.
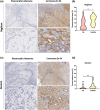
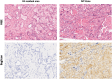
Results: Comparative proteomic analysis revealed 2680 proteins across the three tissue types, with 799 significantly altered between groups. Translocation protein SEC63 homolog, Annexin A6 and Biglycan were up-regulated in CXPA compared to PA. Decorin was markedly up-regulated in both PA and CXPA compared to normal salivary gland (log2 fold changes of 7.58 and 7.38, respectively). Validation confirmed elevated levels of Biglycan and Decorin in the extracellular matrix of CXPA compared to PA.
Conclusions: Proteomic analysis identified differential protein expression patterns associated with malignant transformation of PA into CXPA. Findings indicate a crucial role for extracellular matrix proteins, specifically Biglycan and Decorin, in the tumorigenic progression of PA and CXPA.
Keywords: carcinoma ex‐pleomorphic adenoma; glandular and epithelial; head and neck neoplasms; proteomic; rare diseases.
© 2024 The Author(s). Oral Diseases published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abiko, Y. , Nishimura, M. , Mitamura, J. , Rahemtulla, F. , Scott, P. G. , Dodd, C. M. , Mizoguchi, I. , & Kaku, T. (1999). An immunohistochemical study of the localization of biglycan, decorin and large chondroitin‐sulfate proteoglycan in pleomorphic adenoma. Acta Histochemica et Cytochemica, 32(6), 459–463.
-
- Altemani, A. , Martins, M. T. , Freitas, L. , Soares, F. , Araújo, N. S. , & Araújo, V. C. (2005). Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma (CXPA): Immunoprofile of the cells involved in carcinomatous progression. Histopathology, 46(6), 635–641. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen, S. , Therkildsen, M. H. , Bjørndal, K. , & Homøe, P. (2016). Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland 1985‐2010: A Danish nationwide study of incidence, recurrence rate and malignant transformation. Head & Neck, 38(Suppl 1), E1364–E1369. - PubMed
-
- Bankhead, P. , Loughrey, M. B. , Fernández, J. A. , Dombrowski, Y. , McArt, D. G. , Dunne, P. D. , McQuaid, S. , Gray, R. T. , Murray, L. J. , Coleman, H. G. , James, J. A. , Salto‐Tellez, M. , & Hamilton, P. W. (2017). QuPath: Open‐source software for digital pathology image analysis. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 16878. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carnielli, C. M. , Macedo, C. C. S. , De Rossi, T. , Granato, D. C. , Rivera, C. , Domingues, R. R. , Pauletti, B. A. , Yokoo, S. , Heberle, H. , Busso‐Lopes, A. F. , Cervigne, N. K. , Sawazaki‐Calone, I. , Meirelles, G. V. , Marchi, F. A. , Telles, G. P. , Minghim, R. , Ribeiro, A. C. P. , Brandão, T. B. , de Castro, G., Jr. , … Paes Leme, A. F. (2018). Combining discovery and targeted proteomics reveals a prognostic signature in oral cancer. Nature Communications, 9(1), 3598. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

