Leech Poecilobdella manillensis protein extract ameliorated hyperuricemia by restoring gut microbiota dysregulation and affecting serum metabolites
- PMID: 39156502
- PMCID: PMC11326090
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i29.3488
Leech Poecilobdella manillensis protein extract ameliorated hyperuricemia by restoring gut microbiota dysregulation and affecting serum metabolites
Abstract
Background: Hyperuricemia (HUA) is a public health concern that needs to be solved urgently. The lyophilized powder of Poecilobdella manillensis has been shown to significantly alleviate HUA; however, its underlying metabolic regulation remains unclear.
Aim: To explore the underlying mechanisms of Poecilobdella manillensis in HUA based on modulation of the gut microbiota and host metabolism.
Methods: A mouse model of rapid HUA was established using a high-purine diet and potassium oxonate injections. The mice received oral drugs or saline. Additionally, 16S rRNA sequencing and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics were performed to identify changes in the microbiome and host metabolome, respectively. The levels of uric acid transporters and epithelial tight junction proteins in the renal and intestinal tissues were analyzed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
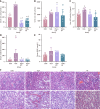
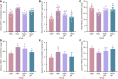
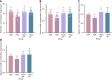
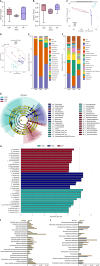
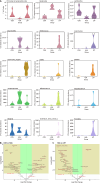
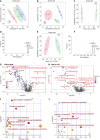
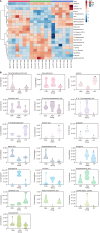
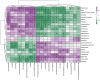
Results: The protein extract of Poecilobdella manillensis lyophilized powder (49 mg/kg) showed an enhanced anti-trioxypurine ability than that of allopurinol (5 mg/kg) (P < 0.05). A total of nine bacterial genera were identified to be closely related to the anti-trioxypurine activity of Poecilobdella manillensis powder, which included the genera of Prevotella, Delftia, Dialister, Akkermansia, Lactococcus, Escherichia_Shigella, Enterococcus, and Bacteroides. Furthermore, 22 metabolites in the serum were found to be closely related to the anti-trioxypurine activity of Poecilobdella manillensis powder, which correlated to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways of cysteine and methionine metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, galactose metabolism, and phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan biosynthesis. Correlation analysis found that changes in the gut microbiota were significantly related to these metabolites.
Conclusion: The proteins in Poecilobdella manillensis powder were effective for HUA. Mechanistically, they are associated with improvements in gut microbiota dysbiosis and the regulation of sphingolipid and galactose metabolism.
Keywords: Galactose metabolism pathway; Gut microbiota; Hyperuricemia; Metabolism; Multi-omics; Poecilobdella manillensis; Sphingolipid metabolism pathway.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Causal effects of gut microbiota on gout and hyperuricemia: insights from genome-wide Mendelian randomization, RNA-sequencing, 16S rRNA sequencing, and metabolomes.Biosci Rep. 2024 Nov 27;44(11):BSR20240595. doi: 10.1042/BSR20240595. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39492788 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of traditional Chinese medicine lyophilized powder of Poecilobdella manillensis in the treatment of hyperuricemia.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Dec 26;12(36):6939-6943. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i36.6939. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39726925 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the effects of rare ginsenosides on hyperuricemia and associated sperm damage via nontargeted metabolomics and gut microbiota.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Oct 5;332:118362. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118362. Epub 2024 May 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38768838
-
Elucidating the role of gut microbiota dysbiosis in hyperuricemia and gout: Insights and therapeutic strategies.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Oct 28;30(40):4404-4410. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i40.4404. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39494101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The gut microbiota as a target to control hyperuricemia pathogenesis: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(14):3979-3989. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1874287. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33480266 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of traditional Chinese medicine extracts in hyperuricemia and gout treatment: Mechanisms and clinical applications.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 21;30(47):5076-5080. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i47.5076. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39713159 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota participates and remodels host metabolism: From treating patients to treating their gut flora.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 7;30(45):4839-4843. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i45.4839. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39649550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao H, Chen X, Zhang L, Meng F, Zhou L, Pang X, Lu Z, Lu Y. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Fmb14 prevents purine induced hyperuricemia and alleviate renal fibrosis through gut-kidney axis. Pharmacol Res. 2022;182:106350. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

