Serum exosomal miR-141-3p and miR-3679-5p levels associated with endotype and postoperative recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
- PMID: 39156601
- PMCID: PMC11327455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.waojou.2024.100938
Serum exosomal miR-141-3p and miR-3679-5p levels associated with endotype and postoperative recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
Abstract
Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is a chronic inflammatory disease. Exosomes were involved in different inflammatory diseases, but their roles in CRSwNP were poorly explored.
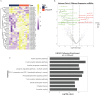
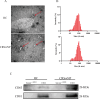
Method: We collected serum samples from 8 CRSwNP patients and 8 healthy controls (HC) and isolated their exosomes. MiRNA sequencing was performed for the exosome samples and differentially expressed miRNAs were identified. The top 3 differentially expressed exosomal miRNAs were confirmed in 2 validation cohorts, and their diagnostic values, predictive values for eosinophilic endotype, and recurrence were evaluated.
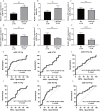
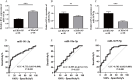
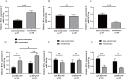
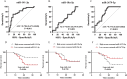
Results: Distinctive serum exosomal miRNA profiles were observed between CRSwNP and HC groups. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction results in the first validation cohort revealed that serum exosomal miR-141-3p levels were increased, and miR-18a-5p and miR-3679-5p levels were decreased in the CRSwNP group compared to the HC group. These 3 miRNAs were further validated in the second validation cohort, and the results showed that miR-141-3p levels were elevated and miR-3679-5p levels were reduced in the serum exosomes in the eosinophilic CRSwNP group in comparison with the non-eosinophilic CRSwNP group. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves highlighted that exosomal miR-141-3p and miR-3679-5p exhibited promising values for predicting the eosinophilic endotype. The patients in the second cohort were followed up for 2 years, and categorized into recurrence and non-recurrence groups. The serum exosomal miR-141-3p levels were increased and miR-3679-5p levels were reduced in the recurrence group in comparison with the non-recurrence group. ROC curves and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed significant associations between the levels of exosomal miR-141-3p and miR-3679-5p and the risk of postoperative recurrence.
Conclusions: This study identified unique miRNA expression patterns in serum exosomes of CRSwNP patients. Circulating exosomal miR-141-3p and miR-3679-5p emerged as novel biomarkers for diagnosing CRSwNP, predicting the eosinophilic endotype, and forecasting postoperative recurrence.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Exosomes; Nasal polyps; Recurrence.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no patents, products in development, or marketed products to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Boscke R., Heidemann M., Bruchhage K.L. Dupilumab for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: real-life retrospective 12-month effectiveness data. Rhinology. 2023;61:203–213. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens W.J., Viskens A.S., Backer V., et al. EPOS/EUFOREA update on indication and evaluation of biologics in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps 2023. Rhinology. 2023;61:194–202. - PubMed
-
- Hellings P.W., Fokkens W.J., Orlandi R., et al. The EUFOREA pocket guide for chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2023;61:85–89. - PubMed
-
- Mueller S.K., Wendler O., Mayr S., et al. Comparison of mucus and serum biomarker sampling in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. International forum of allergy & rhinology. 2024;14:887–897. - PubMed
-
- Rank M.A., Wonnaparhown A.M., Freeman C.M. Recent guidelines addressing chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: practical aspects. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2023;133 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

