Modeling Alzheimer's disease using human cell derived brain organoids and 3D models
- PMID: 39156632
- PMCID: PMC11328153
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1434945
Modeling Alzheimer's disease using human cell derived brain organoids and 3D models
Abstract
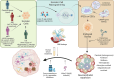
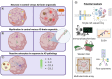
Age-related neurodegenerative diseases, like Alzheimer's disease (AD), are challenging diseases for those affected with no cure and limited treatment options. Functional, human derived brain tissues that represent the diverse genetic background and cellular subtypes contributing to sporadic AD (sAD) are limited. Human stem cell derived brain organoids recapitulate some features of human brain cytoarchitecture and AD-like pathology, providing a tool for illuminating the relationship between AD pathology and neural cell dysregulation leading to cognitive decline. In this review, we explore current strategies for implementing brain organoids in the study of AD as well as the challenges associated with investigating age-related brain diseases using organoid models.
Keywords: APOE; Alzheimer’s disease; aging; amyloid beta; brain organoids; cerebral organoids; hyperphosphorylated tau; neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Fernandes, Revanna, Pratt, Hayes, Marchetto and Gage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Akama K. T., Van Eldik L. J. (2000). β-Amyloid stimulation of inducible nitric-oxide synthase in astrocytes is interleukin-1β- and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα)-dependent, and involves a TNFα receptor-associated factor- and NFκB-inducing kinase- dependent signaling mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 7918–7924. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.11.7918 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alić I., Goh P. A., Murray A., Portelius E., Gkanatsiou E., Gough G., et al. (2021). Patient-specific Alzheimer-like pathology in trisomy 21 cerebral organoids reveals BACE2 as a gene dose-sensitive AD suppressor in human brain. Molecular Psychiatry 26, 5766–5788. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0806-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s Association (2006) ‘Early onset dementia: a national challenge, a future crisis’, Alzheimer’s Association, Washington, DC, (June).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

