CCR3 knockdown attenuates prolonged underwater operations-induced cognitive impairment via alleviating microglia-mediated neuroinflammation
- PMID: 39156650
- PMCID: PMC11326909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110379
CCR3 knockdown attenuates prolonged underwater operations-induced cognitive impairment via alleviating microglia-mediated neuroinflammation
Abstract
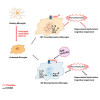
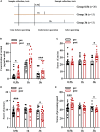
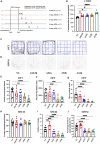
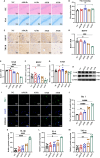
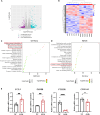
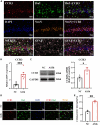
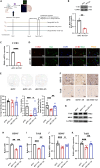
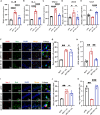
Maintaining cognitive integrity is crucial during underwater operations, which can significantly impact work performance and risk severe accidents. However, the cognitive effects of underwater operations and their underlying mechanism remain elusive, posing great challenges to the medical protection of professionals concerned. Here, we found that a single underwater operation session affects cognition in a time-dependent model. Prolonged exposure elicits significant cognitive impairment and hippocampal dysfunction, accompanied by increased neuroinflammation. Furthermore, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis revealed the involvement of neuroinflammation and highlighted the critical role of CCR3. Knockdown of CCR3 significantly rescued cognitive impairment and hippocampal dysfunction and reversed the upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, by switching the activated microglia from a pro-inflammatory to a neuroprotective phenotype. Taken together, these results highlighted the time-dependent effects of a single underwater operation session on cognitive function. Knocking down CCR3 can attenuate neuroinflammation by regulating polarization of activated microglia, thereby alleviating prolonged underwater operations-induced cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Neuroscience; Sensory neuroscience; Systems neuroscience.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hammerton Z. Determining the variables that influence SCUBA diving impacts in eastern Australian marine parks. Ocean Coast Manag. 2017;142:209–217.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

