Focal dermal hypoplasia (Goltz Syndrome): A preterm neonate with multisystem anomalies-A case report
- PMID: 39157028
- PMCID: PMC11329961
- DOI: 10.1177/2050313X241274981
Focal dermal hypoplasia (Goltz Syndrome): A preterm neonate with multisystem anomalies-A case report
Abstract
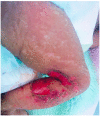
Goltz syndrome is a rare condition characterized by thinning of the skin, which leads to the herniation of fat and results in both skin and systemic abnormalities. The primary cause of this syndrome is the mutation of the PORCN gene, which is associated with the X chromosome. A newborn baby was admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit due to skeletal and skin abnormalities. The major findings in this patient included anophthalmia, microform cleft lip, subcutaneous fat herniation, and split foot. An abdominal ultrasound examination revealed a solitary right kidney and an echocardiogram showed patent ductus arteriosus. The patient was treated for neonatal sepsis, and the family received counseling about the disease. We report this case because of its exceptional rarity.
Keywords: Focal dermal hypoplasia; fat herniation; solitary kidney; split foot.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Bostwick B, Van den Veyver IB, Sutton VR. Focal dermal hypoplasia. GeneReviews (®). 1993. May 15.
-
- Tejani Z, Batra P, Mason C, et al. Focal dermal hypoplasia: oral and dental findings. J Clin Pediatr Dent 2006; 30(1): 67–72. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Jin X, Zhao X, et al. Focal dermal hypoplasia: updates. Oral Dis 2014; 20(1): 17–24. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources