A deep learning approach to dysphagia-aspiration detecting algorithm through pre- and post-swallowing voice changes
- PMID: 39157445
- PMCID: PMC11327512
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1433087
A deep learning approach to dysphagia-aspiration detecting algorithm through pre- and post-swallowing voice changes
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to identify differences in voice characteristics and changes between patients with dysphagia-aspiration and healthy individuals using a deep learning model, with a focus on under-researched areas of pre- and post-swallowing voice changes in patients with dysphagia. We hypothesized that these variations may be due to weakened muscles and blocked airways in patients with dysphagia.
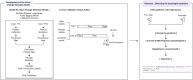
Methods: A prospective cohort study was conducted on 198 participants aged >40 years at the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital from October 2021 to February 2023. Pre- and post-swallowing voice data of the participants were converted to a 64-kbps mp3 format, and all voice data were trimmed to a length of 2 s. The data were divided for 10-fold cross-validation and stored in HDF5 format with anonymized IDs and labels for the normal and aspiration groups. During preprocessing, the data were converted to Mel spectrograms, and the EfficientAT model was modified using the final layer of MobileNetV3 to effectively detect voice changes and analyze pre- and post-swallowing voices. This enabled the model to probabilistically categorize new patient voices as normal or aspirated.
Results: In a study of the machine-learning model for aspiration detection, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) values were analyzed across sexes under different configurations. The average AUC values for males ranged from 0.8117 to 0.8319, with the best performance achieved at a learning rate of 3.00e-5 and a batch size of 16. The average AUC values for females improved from 0.6975 to 0.7331, with the best performance observed at a learning rate of 5.00e-5 and a batch size of 32. As there were fewer female participants, a combined model was developed to maintain the sex balance. In the combined model, the average AUC values ranged from 0.7746 to 0.7997, and optimal performance was achieved at a learning rate of 3.00e-5 and a batch size of 16.
Conclusion: This study evaluated a voice analysis-based program to detect pre- and post-swallowing changes in patients with dysphagia, potentially aiding in real-time monitoring. Such a system can provide healthcare professionals with daily insights into the conditions of patients, allowing for personalized interventions.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier NCT05149976.
Keywords: aspiration detection model; deep learning; dysphagia-aspiration; voice changes pre-and post-swallowing; voice-based non-face-to-face monitoring.
Copyright © 2024 Kim, Kim, Choi, Lee and Ryu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Analysis to Automatically Detect the Presence of Penetration or Aspiration in Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study.J Korean Med Sci. 2022 Feb 14;37(6):e42. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e42. J Korean Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35166079 Free PMC article.
-
Machine-learning assisted swallowing assessment: a deep learning-based quality improvement tool to screen for post-stroke dysphagia.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 24;17:1302132. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1302132. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38130696 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of voice changes due to aspiration via acoustic voice analysis.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018 Aug;45(4):801-806. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018. PMID: 29097046
-
Swallowing therapy for dysphagia in acute and subacute stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 30;10(10):CD000323. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000323.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30376602 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Prevalence of Dysphagia in Patients with Mild COVID-19 and Those with Aspiration Pneumonia Alone: Findings of the Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 18;59(10):1851. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101851. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893569 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosis and Treatment of Dysphagia.Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jan 23;29(1):1-2. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1801781. eCollection 2025 Jan. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39850498 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Machine Learning Pipeline for Automated Bolus Segmentation and Area Measurement in Swallowing Videofluoroscopy Images of an Infant Pig Model.Dysphagia. 2025 Apr 28:10.1007/s00455-025-10829-z. doi: 10.1007/s00455-025-10829-z. Online ahead of print. Dysphagia. 2025. PMID: 40293507
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

