Myopericarditis Following Use of Selective Androgen Receptor Modifier "RAD-140"
- PMID: 39157568
- PMCID: PMC11328744
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2024.102423
Myopericarditis Following Use of Selective Androgen Receptor Modifier "RAD-140"
Abstract
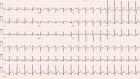
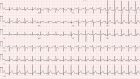
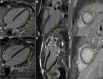
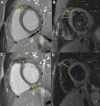
We report the case of a 16-year-old boy who had myopericarditis following the first dose of a selective androgen receptor modulator called Testolone ("RAD-140"). These drugs are widely abused by physically active young adults; however, the drugs' side effects, which can be life-threatening, are not well characterized.
Keywords: RAD-140; Testolone modulator; myocarditis; selective androgen receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Poff R.M., Gardner C.E. Building the body up just to break the body down: a look into black market substance use among young athletes and bodybuilders. J Urgent Care Med. 2021;15(7):11–14.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

