Monitoring of molecular responses to tirabrutinib in a cohort of exceptional responders with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma
- PMID: 39157626
- PMCID: PMC11327755
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.966
Monitoring of molecular responses to tirabrutinib in a cohort of exceptional responders with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma
Conflict of interest statement
Martin J. S. Dyer has received research funding from Gilead Sciences. Harriet S. Walter has received research funding from Gilead Sciences. Sandrine Jayne has received research funding from Gilead Sciences. All the other authors declare no conflict of interest.
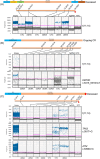
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
