Outcome of 421 adult patients with Philadelphia-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated under an intensive program inspired by the GIMEMA LAL1913 clinical trial: a Campus ALL study
- PMID: 39157875
- PMCID: PMC11694127
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285638
Outcome of 421 adult patients with Philadelphia-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated under an intensive program inspired by the GIMEMA LAL1913 clinical trial: a Campus ALL study
Abstract
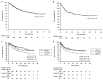
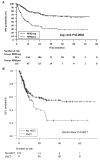
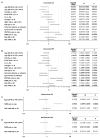
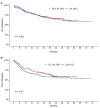
The introduction of pediatric-inspired regimens in adult Philadelphia-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph- ALL) has significantly improved patients' prognosis. Within the Campus ALL network, we analyzed the outcome of adult Ph- ALL patients treated according to the GIMEMA LAL1913 protocol outside the clinical trial to compare the real-life data with the study results. We included 421 consecutive patients; median age 42 years. The complete remission (CR) rate after the first course of chemotherapy was 94%, and measurable residual disease (MRD) negativity after the third course was achieved in 72% of patients. The 3-year overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were 67% and 57%, respectively. In a multivariate analysis, MRD positivity negatively influenced DFS. In a time-dependent analysis including only very high-risk (VHR) and MRD positive cases, transplanted (hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [HSCT]) patients had a significantly better DFS than non-HSCT patients (P=0.0017). During induction, grade ≥2 pegaspargase-related hepato-toxicity was observed in 25% of patients (vs. 12% in the GIMEMA LAL1913 trial, P=0.0003). In this large, real-life cohort of Ph- ALL, we confirmed the very high CR rate and a superimposable OS and DFS compared to the GIMEMA LAL1913 clinical trial (CR rate after C1, 94% vs. 85%, P=0.0004; 3-year OS, 67% vs. 67%, P=0.94; 3-year DFS, 57% vs. 63%, P=0.17). HSCT confirms its important role in VHR and MRD-positive patients. The rate of pegaspargase-related toxicity was significantly higher in the real-life setting, emphasizing the importance of dose adjustment in the presence of risk factors to avoid excessive toxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Huguet F, Leguay T, Raffoux E, et al. . Pediatric-inspired therapy in adults with Philadelphia chromosome negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the GRAALL-2003 study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(6):911-918. - PubMed
-
- Huguet F, Chevret S, Leguay T, et al. . Intensified therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: report of the randomized GRAALL-2005 clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(24):2514-2523. - PubMed
-
- Toft N, Birgens H, Abrahamsson J, et al. . Results of NOPHO ALL2008 treatment for patients aged 1-45 years with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2018;32(3):606-615. - PubMed

