Self-injury and suicide among people living with HIV/AIDS in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39160497
- PMCID: PMC11334318
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-19444-3
Self-injury and suicide among people living with HIV/AIDS in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of self-injury and suicide is higher than the general population of people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA). However, the results reported in existing studies are highly variable in China. The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to synthesize the currently available high-quality evidence to explore the prevalence and influence factors of self-injury and suicide among PLWHA in China.
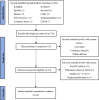
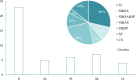
Method: We retrieve literature written in Chinese and English through databases such as PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, SinoMed, CNKI, WanFang Database, and CQVIP from inception to 1 September 2022. Sata 16.0 software was used for analysis.
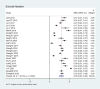
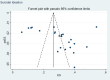
Results: A total of 28 studies were included with a sample size of 1,433,971 and had a satisfactory quality score of ≥ 5. The prevalence among PLWHA in China were 30% for suicidal ideation (SI), 5% for suicide attempt (SA), 8% for suicide plan (SP), 7% for attempted suicide (AS), and 3‰ for completed suicide. High stigma (OR = 2.94, 95%CI: 1.90 - 4.57), depression (OR, 3.17; 95%CI, 2.20 - 4.57), anxiety (OR, 3.06; 95%CI, 2.23 - 4.20), low self-esteem (OR, 3.82, 95%CI, 2.22 - 6.57), high HIV related stress (OR, 2.53; 95%CI, 1.36 - 4.72), and unemployment (OR, 2.50; 95%CI, 1.51 - 4.15) are risk factors for SI; high social support (OR, 0.61; 95%CI, 0.44 - 0.84) and spouse infected with HIV (OR, 0.39; 95%CI, 0.21 - 0.74) are protective factors for SI; depression (OR, 1.62; 95%CI, 1.24 - 2.13), high aggression (OR, 4.66; 95%CI, 2.59 - 8.39), and more negative life events (OR, 2.51; 95%CI, 1.47 - 4.29) are risk factors for AS; high level of education (OR, 1.31; 95%CI, 1.21 - 1.43) is risk factor for CS.
Conclusion: Figures indicate that approximately one-third of PLWHA had suicidal ideation, and three out of 1,000 completed suicide in China. Positive events are protective factors for self-injury and suicide among PLWHA, while negative events are risk factors. This suggests that psychosocial support and risk assessment should be integrated into the care of PLWHA.
Keywords: HIV/AIDS; Meta-analysis; Prevalence; Risk factors; Self-injury; Suicide.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Psychosocial health and suicidal ideation among people living with HIV/AIDS: A cross-sectional study in Nanjing, China.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 22;13(2):e0192940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192940. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29470532 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological pathway to suicidal ideation among people living with HIV/AIDS in China: A structural equation model.Psychiatry Res. 2018 Feb;260:255-261. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.11.077. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Psychiatry Res. 2018. PMID: 29220683
-
Suicidal ideation among attendees of a West African HIV clinic.Arch Suicide Res. 2015;19(1):103-16. doi: 10.1080/13811118.2014.915776. Arch Suicide Res. 2015. PMID: 25058473
-
Suicidal ideation, attempt, and its associated factors among adult HIV/AIDS patients in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis study.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 14;19(3):e0294078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294078. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38484019 Free PMC article.
-
Suicidal ideation and associated factors among people living with HIV/AIDS in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 10;15:1361304. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1361304. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39319360 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Navigating Turbulent Waves of Emotions: Multi-Level Stress and Coping Among Chinese Men Who Have Sex with Men Living with HIV.Glob Qual Nurs Res. 2024 Oct 21;11:23333936241292739. doi: 10.1177/23333936241292739. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Glob Qual Nurs Res. 2024. PMID: 39463800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Mental Health and Substance Use (who.int). Available: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mental-health.
-
- World Health Organization. Summary of the global HIV epidemic. 2021. Available: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/hiv-aids.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

