The causal effect of gut microbiota on hepatic encephalopathy: a mendelian randomization analysis
- PMID: 39160503
- PMCID: PMC11334368
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-024-01939-y
The causal effect of gut microbiota on hepatic encephalopathy: a mendelian randomization analysis
Abstract
Background: There is growing evidence for a relationship between gut microbiota and hepatic encephalopathy (HE). However, the causal nature of the relationship between gut microbiota and HE has not been thoroughly investigated.
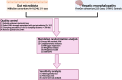
Method: This study utilized the large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWAS) summary statistics to evaluate the causal association between gut microbiota and HE risk. Specifically, two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) approach was used to identify the causal microbial taxa for HE. The inverse variance weighted (IVW) method was used as the primary MR analysis. Sensitive analyses were performed to validate the robustness of the results.
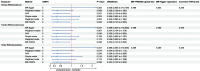
Results: The IVW method revealed that the genus Bifidobacterium (OR = 0.363, 95% CI: 0.139-0.943, P = 0.037), the family Bifidobacteriaceae (OR = 0.359, 95% CI: 0.133-0.950, P = 0.039), and the order Bifidobacteriales (OR = 0.359, 95% CI: 0.133-0.950, P = 0.039) were negatively associated with HE. However, no causal relationship was observed among them after the Bonferroni correction test. Neither heterogeneity nor horizontal pleiotropy was found in the sensitivity analysis.
Conclusion: Our MR study demonstrated a potential causal association between Bifidobacterium, Bifidobacteriaceae, and Bifidobacteriales and HE. This finding may provide new therapeutic targets for patients at risk of HE in the future.
Keywords: Causal relationship; Gut microbiota; Gut-liver-brain axis; Hepatic encephalopathy; Mendelian randomization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic liability of gut microbiota for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung function: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 22;14:1348685. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1348685. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38841114 Free PMC article.
-
The causal relationship between gut microbiota and neuroblastoma: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis and meta-analysis.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Apr 2;12(4):e0365623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03656-23. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38411074 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota and autism spectrum disorders: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Dec 14;13:1267721. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1267721. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38156319 Free PMC article.
-
The causal relationships between gut microbiota and venous thromboembolism: a Mendelian randomization study.Hereditas. 2025 Feb 20;162(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00389-5. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 39980076 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential causal relationship between gut microbiota and heart failure: A two-sample mendelian randomization study combined with the geo database.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Feb;49(2):102235. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102235. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38040216 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Role of High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Stress Urinary Incontinence with Special Emphasis on Overweight/Obese Individuals.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Jul 11;22(13):3304-3315. doi: 10.7150/ijms.116324. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40765569 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

