Dendritic cells transfected with DNA constructs encoding CCR9, IL-10, and type II collagen demonstrate induction of immunological tolerance in an arthritis model
- PMID: 39161770
- PMCID: PMC11330828
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447897
Dendritic cells transfected with DNA constructs encoding CCR9, IL-10, and type II collagen demonstrate induction of immunological tolerance in an arthritis model
Abstract
Introduction: Restoring immune tolerance is a promising area of therapy for autoimmune diseases. One method that helps restore immunological tolerance is the approach using tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDCs). In our study, we analyzed the effectiveness of using dendritic cells transfected with DNA constructs encoding IL-10, type II collagen, and CCR9 to induce immune tolerance in an experimental model of arthritis.
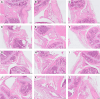
Methods: Dendritic cell cultures were obtained from bone marrow cells of Balb/c mice. Dendritic cells (DCs) cultures were transfected with pmaxCCR9, pmaxIL-10, and pmaxCollagen type II by electroporation. The phenotype and functions of DCs were studied using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and flow cytometry. Migration of electroporated DCs was assessed in vitro. Induction of antigen-collagen induced arthritis (ACIA) was carried out according to the protocol in Balb/c mice. DCs were then administered to ACIA mice. The development of arthritis was monitored by measuring paw swelling with a caliper at different time points. The immunological changes were assessed by analyzing the content of antibodies to type II collagen using enzyme immunoassay. Additionally, a histological examination of the joint tissue was conducted, followed by data analysis.
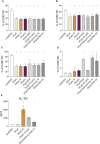
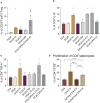
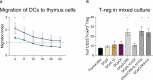
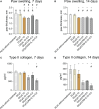
The results are as follows: DCs were obtained, characterized by reduced expression of CD80, CD86, and H-2Db (MHC class I), increased expression of CCR9, as well as producing IL-10 and having migratory activity to thymus cells. Transfected DCs induced T-regulatory cells (T-reg) and increased the intracellular content of IL-10 and TGF-β in CD4+T cells in their co-culture, and also suppressed their proliferative activity in response to antigen. The administration of tolDCs transfected with DNA constructs encoding type II collagen, IL-10, and CCR9 to mice with ACIA demonstrated a reduction in paw swelling, a reduction in the level of antibodies to type II collagen, and a regression of histological changes.
Conclusion: The study presents an approach by which DCs transfected with DNA constructs encoding epitopes of type II collagen, IL-10 and CCR9 promote the development of antigen-specific tolerance, control inflammation and reduce the severity of experimental arthritis through the studied mechanisms: induction of T-reg, IL-10, TGF-β.
Keywords: DNA-constructs; T-regulatory cells; antigen-specific dendritic cells; experimental arthritis; immunological tolerance; tolerant dendritic cells.
Copyright © 2024 Fisher, Kurilin, Bulygin, Shevchenko, Philippova, Taranov, Ivleva, Maksyutov and Sennikov.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The murine DCs transfected with DNA-plasmid encoding CCR9 demonstrate the increased migration to CCL25 and thymic cells in vitro and to the thymus in vivo.Cytokine. 2021 Jun;142:155473. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155473. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 33647585
-
Dendritic cells modulated by innate immunity improve collagen-induced arthritis and induce regulatory T cells in vivo.Immunology. 2009 Jan;126(1):35-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02875.x. Epub 2008 Aug 27. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 18754812 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells are involved in the generation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in Peyer's patches in an orally tolerized, collagen-induced arthritis mouse model.Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(1):R11. doi: 10.1186/ar2361. Epub 2008 Jan 25. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 18221522 Free PMC article.
-
Type II collagen oral tolerance; mechanism and role in collagen-induced arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19(6):581-9. doi: 10.1007/s10165-009-0210-0. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Mod Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19697097 Review.
-
Tolerogenic Immunotherapy: Targeting DC Surface Receptors to Induce Antigen-Specific Tolerance.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 19;12:643240. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.643240. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
T-regulatory cells for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 4;16:1511671. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1511671. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39967659 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lortholary O, Fernandez-Ruiz M, Baddley JW, Manuel O, Mariette X, Winthrop KL. Infectious complications of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis during targeted and biological therapies: a viewpoint in 2020. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79.12:1532–43. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217092 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huss V, Bower H, Wadström H, Frisell T, Askling J ,, ARTIS group . Short-and longer-term cancer risks with biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs as used against rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice. Rheumatology. (2022) 6:1810–8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab570 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Greenberg JD, Reed G, Kremer JM, Tindall E, Kavanaugh A, Zheng C, et al. . Association of methotrexate and tumour necrosis factor antagonists with risk of infectious outcomes including opportunistic infections in the CORRONA registry. Ann rheumatic Dis. (2010) 69.2:380–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.089276 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

