Off-axis digital lensless holographic microscopy based on spatially multiplexed interferometry
- PMID: 39161785
- PMCID: PMC11331263
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.29.S2.S22715
Off-axis digital lensless holographic microscopy based on spatially multiplexed interferometry
Abstract
Significance: Digital holographic microscopy (DHM) is a label-free microscopy technique that provides time-resolved quantitative phase imaging (QPI) by measuring the optical path delay of light induced by transparent biological samples. DHM has been utilized for various biomedical applications, such as cancer research and sperm cell assessment, as well as for in vitro drug or toxicity testing. Its lensless version, digital lensless holographic microscopy (DLHM), is an emerging technology that offers size-reduced, lightweight, and cost-effective imaging systems. These features make DLHM applicable, for example, in limited resource laboratories, remote areas, and point-of-care applications.
Aim: In addition to the abovementioned advantages, in-line arrangements for DLHM also include the limitation of the twin-image presence, which can restrict accurate QPI. We therefore propose a compact lensless common-path interferometric off-axis approach that is capable of quantitative imaging of fast-moving biological specimens, such as living cells in flow.
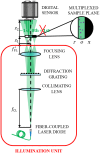
Approach: We suggest lensless spatially multiplexed interferometric microscopy (LESSMIM) as a lens-free variant of the previously reported spatially multiplexed interferometric microscopy (SMIM) concept. LESSMIM comprises a common-path interferometric architecture that is based on a single diffraction grating to achieve digital off-axis holography. From a series of single-shot off-axis holograms, twin-image free and time-resolved QPI is achieved by commonly used methods for Fourier filtering-based reconstruction, aberration compensation, and numerical propagation.
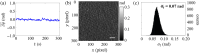
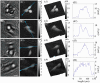
Results: Initially, the LESSMIM concept is experimentally demonstrated by results from a resolution test chart and investigations on temporal stability. Then, the accuracy of QPI and capabilities for imaging of living adherent cell cultures is characterized. Finally, utilizing a microfluidic channel, the cytometry of suspended cells in flow is evaluated.
Conclusions: LESSMIM overcomes several limitations of in-line DLHM and provides fast time-resolved QPI in a compact optical arrangement. In summary, LESSMIM represents a promising technique with potential biomedical applications for fast imaging such as in imaging flow cytometry or sperm cell analysis.
Keywords: digital holographic microscopy; digital lensless holographic microscopy; label-free imaging; off-axis lensless holography; phase retrieval; quantitative phase imaging; spatially multiplexed interferometric microscopy.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures




References
-
- Kim M. K., Digital holographic microscopy. Principles, techniques, and applications, Springer US; (2011).
-
- Park Y. K., Depeursinge C., Popescu G., “Quantitative phase imaging in biomedicine,” Nat. Photonics 12(10), 578–589 (2018). 10.1038/s41566-018-0253-x - DOI
-
- Kemper B., et al. , “Label-free quantitative in vitro live cell imaging with digital holographic microscopy,” in Bioanalytical Reviews, Wegener J., Ed., Vol. 2, Springer, Cham: (2019).
-
- Zernike F., “Phase contrast, a new method for the microscopic observation of transparent objects,” Physica 9(7), 686–698 (1942). 10.1016/S0031-8914(42)80035-X - DOI
-
- Allen R., David G., Nomarski G., “The Zeiss-Nomarski differential interference equipment for transmitted-light microscopy,” Zeitschrift fur wissenschaftliche Mikroskopie 69(4), 193–221 (1969). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

