Influence of bundled care treatment on functional outcome in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage
- PMID: 39161870
- PMCID: PMC11330843
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1357815
Influence of bundled care treatment on functional outcome in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage
Abstract
Background and aims: General guideline recommendations in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) include blood pressure-, temperature- and glucose management. The therapeutic effect of such a "care bundle" (blood pressure lowering, glycemic control, and treatment of pyrexia) on clinical outcomes becomes increasingly established. For the present study, we aimed to investigate associations of strict bundled care treatment (BCT) with clinical outcomes and characterize associations with key outcome effectors such as hematoma enlargement (HE) and peak perihemorrhagic edema (PHE).
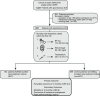
Methods: We screened consecutive ICH patients (n = 1,322) from the prospective UKER-ICH cohort study. BCT was defined as achieving and maintaining therapeutic ranges for systolic blood pressure (110-160 mmHg), glucose (80-180 mg/dL), and body temperature (35.5-37.5°C) over the first 72 h. The primary outcome was the functional outcome at 12 months (modified Rankin Scale (mRS) 0-3). Secondary outcomes included mortality at 12 months, the occurrence of hematoma enlargement, and the development of peak perihemorrhagic edema. Confounding was addressed by a doubly robust methodology to calculate the absolute treatment effect (ATE) and by calculating e-values.
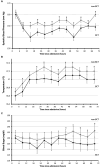
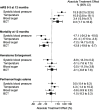
Results: A total of 681 patients remained for analysis, and 182 patients fulfilled all three BCT criteria and were compared to 499 controls. The ATE of BCT to achieve the primary outcome was 9.3%, 95% CI (1.7 to 16.9), p < 0.001; e-value: 3.1, CI (1.8). Mortality at 12 months was significantly reduced by BCT [ATE: -12.8%, 95% CI (-19.8 to -5.7), p < 0.001; e-value: 3.8, CI (2.2)], and no association was observed for HE or peak PHE. Significant drivers of BCT effect on the primary outcome were systolic blood pressure control (ATE: 15.9%) and maintenance of normothermia (ATE: 10.9%).
Conclusion: Strict adherence to this "care bundle" over the first 72 h during acute hospital care in patients with ICH was independently associated with improved functional long-term outcome, driven by systolic blood pressure control and maintenance of normothermia. Our findings strongly warrant prospective validation to determine the generalizability especially in Western countries.Clinical trial registration:ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier [ID: NCT03183167].
Keywords: HE; ICH; PHE; bundle; treatment.
Copyright © 2024 Mrochen, Song, Harders, Sembill, Sprügel, Hock, Lang, Engelhorn, Kallmünzer, Volbers and Kuramatsu.
Conflict of interest statement
AM reports personal fees from Alexion Pharma Germany GmbH, outside the submitted work. BV reports personal fees from Pfizer AG/Bristol-Myers Squibb SA, personal fees from Bayer AG, grants from Institutional grant (Inselspital), personal fees from Ipsen Pharma, personal fees from CSL Behring, outside the submitted work. JK reports personal fees from Beohringer Ingelheim, personal fees from Biogen, personal fees from Boston Scientific, personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Bayer AG, personal fees from Alexion, outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Greenberg SM, Ziai WC, Cordonnier C, Dowlatshahi D, Francis B, Goldstein JN, et al. 2022 Guideline for the Management of Patients with Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2022) 53:e282–361. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000407, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

