Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb. extracts and celastrol alleviate NAFLD by preserving mitochondrial function through activating the FGF21/AMPK/PGC-1α pathway
- PMID: 39161898
- PMCID: PMC11330833
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1444117
Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb. extracts and celastrol alleviate NAFLD by preserving mitochondrial function through activating the FGF21/AMPK/PGC-1α pathway
Abstract
Objective: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent chronic liver disease globally, characterized by the accumulation of lipids, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction in the liver. Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb. (COT) and its active compound celastrol (CEL) have demonstrated antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Our prior research has shown the beneficial effects of COT in mitigating NAFLD induced by a high-fat diet (HFD) in guinea pigs by reducing hepatic lipid levels and inhibiting oxidative stress. This study further assessed the effects of COT on NAFLD and explored its underlying mitochondria-related mechanisms.
Methods: COT extract or CEL was administered as an intervention in C57BL/6J mice fed a HFD or in HepG2 cells treated with sodium oleate. Oral glucose tolerance test, biochemical parameters including liver enzymes, blood lipid, and pro-inflammatory factors, and steatosis were evaluated. Meanwhile, mitochondrial ultrastructure and indicators related to oxidative stress were tested. Furthermore, regulators of mitochondrial function were measured using RT-qPCR and Western blot.
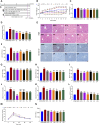
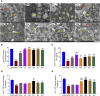
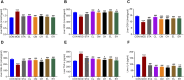
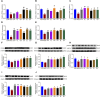
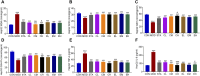
Results: The findings demonstrated significant reductions in hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation associated with NAFLD in both experimental models following treatment with COT extract or CEL. Additionally, improvements were observed in mitochondrial structure, ATP content, and ATPase activity. This improvement can be attributed to the significant upregulation of mRNA and protein expression levels of key regulators including FGF21, AMPK, PGC-1α, PPARγ, and SIRT3.
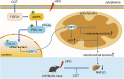
Conclusion: These findings suggest that COT may enhance mitochondrial function by activating the FGF21/AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway to mitigate NAFLD, which indicated that COT has the potential to target mitochondria and serve as a novel therapeutic option for NAFLD.
Keywords: Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb.; FGF21/AMPK/PGC-1α; NAFLD; celastrol; mitochondrial function.
Copyright © 2024 Xue, Liu, Liu, Jia, Fang, Qin and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

