Plasticity of the heart in response to changes in physical activity
- PMID: 39162309
- PMCID: PMC12306423
- DOI: 10.1113/JP284158
Plasticity of the heart in response to changes in physical activity
Abstract
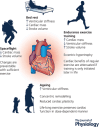
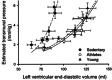
The human heart is very adaptable, with chamber size, wall thickness and ventricular stiffness all modified by periods of inactivity or exercise training. Herein, we summarize the cardiac adaptations induced by changes in physical activity, ranging from bed rest and spaceflight to endurance exercise training, while also highlighting how the ageing process (a long-term model of inactivity) affects cardiac plasticity. Severe inactivity during bed rest or spaceflight leads to cardiac atrophy and ventriculo-vascular stiffening. Conversely, endurance training induces eccentric hypertrophy and enhances ventricular compliance, and can be used as an effective countermeasure to prevent adverse cardiac changes during prolonged periods of bed rest or spaceflight. With sedentary ageing, the heart undergoes concentric remodelling and irreversibly stiffens at advanced age. Specifically, older adults who initiate endurance training later in life are unable to improve ventricular compliance and diastolic function, suggesting reduced cardiac plasticity with advanced age; however, lifelong exercise training prevents age-associated cardiac remodelling and maintains cardiac compliance of older adults at a level similar to those of younger healthy individuals. Nevertheless, there are still many knowledge gaps related to cardiac remodelling and changes in cardiac function induced by bed rest, exercise training and spaceflight, as well as how these different stimuli may interact with advancing age. Future studies should focus on understanding what factors (sex, age, heritability, etc.) may influence the heart's responsiveness to training or deconditioning, as well as understanding the long-term cardiac consequences of spaceflight beyond low-Earth orbit with the added stimulus of galactic cosmic radiation.
Keywords: ageing; astronaut; bed rest; endurance exercise training; inactivity.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Journal of Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson, J. L. , Adams, C. D. , Antman, E. M. , Bridges, C. R. , Califf, R. M. , Casey, D. E. , Chavey, W. E. , Fesmire, F. M. , Hochman, J. S. , Levin, T. N. , Lincoff, A. M. , Peterson, E. D. , Theroux, P. , Wenger, N. K. , & Wright, R. S. (2013). 2012 ACCF/AHA focused update incorporated into the ACCF/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non‐ST‐elevation myocardial infarction: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 61(23), e179–e347. - PubMed
-
- Arbab‐Zadeh, A. , Dijk, E. , Prasad, A. , Fu, Q. , Torres, P. , Zhang, R. , Thomas, J. D. , Palmer, D. , & Levine, B. D. (2004). Effect of aging and physical activity on left ventricular compliance. Circulation, 110(13), 1799–1805. - PubMed
-
- Arbeille, P. , Fomina, G. , Roumy, J. , Alferova, I. , Tobal, N. , & Herault, S. (2001). Adaptation of the left heart, cerebral and femoral arteries, and jugular and femoral veins during short‐ and long‐term head‐down tilt and spaceflights. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 86(2), 157–168. - PubMed
-
- Baevsky, R. M. , Baranov, V. M. , Funtova, I. I. , Diedrich, A. , Pashenko, A. V. , Chernikova, A. G. , Drescher, J. , Jordan, J. , & Tank, J. (2007). Autonomic cardiovascular and respiratory control during prolonged spaceflights aboard the International Space Station. Journal of Applied Physiology, 103(1), 156–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RGPIN-2023-03719/Canadian Government | Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC)
- 80NSSC20K0987/National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- UH1-161690/Canadian Government | Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR)
- 201911FBD-434513-72081/Canadian Government | Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR)
- 5R01AG017479/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
