Low circulating levels of neuregulin 4 as a potential biomarker associated with the severity and prognosis of obesity-related metabolic diseases: a systematic review
- PMID: 39162358
- PMCID: PMC11340757
- DOI: 10.1080/21623945.2024.2390833
Low circulating levels of neuregulin 4 as a potential biomarker associated with the severity and prognosis of obesity-related metabolic diseases: a systematic review
Abstract
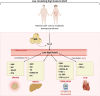
Background: Neuregulin 4 (Nrg4) is a brown adipose tissue-derived adipokine that greatly affects systemic metabolism and improves metabolic derangements. Although abnormal circulating levels of Nrg4 are common in obesity, it remains elusive whether low or elevated levels of this batokine are associated with the onset of metabolic diseases.
Aim: To assess Nrg4 levels and its role as a feasible biomarker to predict the severity of obesity, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and cardiovascular diseases (CVD).
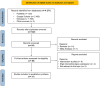
Methods: A search for relevant studies was performed systematically using prominent search engines, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and Embase, by following PRISMA guidelines.
Results: Ample clinical evidence reported low serum/plasma levels of Nrg4 in obesity and these were inversely proportional to the indices of metabolic syndrome, including body mass index, waist circumference, triglycerides, fasting plasma glucose, and homoeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance as well as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. Low circulating Nrg4 levels may aid in the prediction of morbid obesity, and subsequent GDM, T2DM, NAFLD, and CVD.
Conclusion: Current clinical evidence emphasizes that the circulating levels of Nrg4 are decreased in morbid obesity, and it also highlights that Nrg4 May serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for obesity-related metabolic diseases.
Keywords: Neuregulin 4; brown adipose tissue; cardiovascular diseases; diabetes mellitus; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of serum neuregulin 4 (NRG-4) levels on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 9;25(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04097-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40634833 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Neuregulin 4 on Metabolic Dysregulation in Lipodystrophy.Endocrinology. 2025 Jul 8;166(9):bqaf112. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaf112. Endocrinology. 2025. PMID: 40580113 Free PMC article.
-
Statins for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 27;2013(12):CD008623. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008623.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24374462 Free PMC article.
-
Different intensities of glycaemic control for women with gestational diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 10;10(10):CD011624. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011624.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37815094 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin secretagogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in persons at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 17;10(10):CD012151. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012151.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27749986 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictive study of machine learning combined with serum Neuregulin 4 levels for hyperthyroidism in type II diabetes mellitus.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 16;15:1595553. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1595553. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40740865 Free PMC article.
-
The role of novel inflammation-associated biomarkers in diabetic peripheral neuropathy.Metabol Open. 2024 Nov 1;24:100328. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2024.100328. eCollection 2024 Dec. Metabol Open. 2024. PMID: 39559514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipokines as Cardioprotective Factors: BAT Steps Up to the Plate.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 13;13(3):710. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030710. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secreted proteins in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: from bench towards bedside.Protein Cell. 2025 Aug 7;16(8):641-666. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwaf027. Protein Cell. 2025. PMID: 40243151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noncommunicable diseases. n.d. [cited 2024 Feb 10]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
